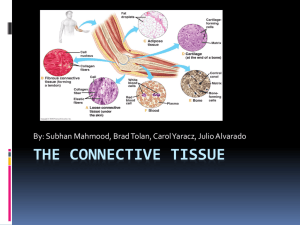
Organization of Tissue Connective Tissue
advertisement
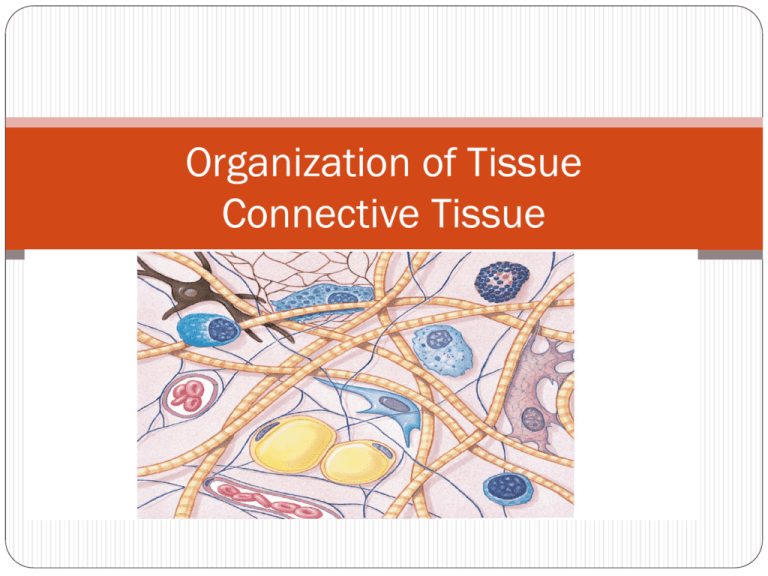
Organization of Tissue Connective Tissue Definition of Connective Tissue Used to connect…. Examples include basement membrane, bone, fat and blood Uses include: Support Structure Storage of energy And transport Composed of three parts Specialized cells Fibers (protein) Ground substance (fluid) matrix Socrative room #701439 1. What is your name (last, first) 2. What are some functions of connective tissues? 3. What components do all connective tissues contain? Specific Functions Through out body, but never exposed Highly vascular Contain sensory receptors Establishing structural framework Transporting fluids and dissolved materials Protecting delicate organs Support, surround and interconnect other tissues Store energy as triglycerides Defense from invading microorganisms Classification of Connective Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Many types of cells, fibers in syrupy ground substance Loose CT (adipose) Dense CT (tendon) Fluid Connective Tissue Distinct populations of cells in watery matrix with dissolved proteins Blood and lymph Supporting Connective Tissue Less cells, more fibers Cartilage and bone Socrative continued 4. list three types of connective tissue 5. give 2 examples of CT proper 6. give 2 examples of fluid CT 7. give 2 examples of supporting CT Connective Tissue Proper Cell Types Fibroblasts Always present Most abundant Makes many proteins Fibrocytes #2 abundance Source of fibers Collagen Reticular Elastic Adipocytes Fat cells Mesenchymal cells Stem cells; differentiate Found in embryonic CT Macrophages Amoeboid (engulf or eat) Immunity Mast cells Mobile Near blood vessels Make histamine and heparin Lymphocytes Produce antibodies Microphages Also phagocytic Melanocytes Make melanin Fibers Collagen Long, straight, unbranched Bundle of proteins Flexible but strong Found in tendons (muscle to bone) and ligaments (bone to bone) Stronger than steel; more likely to break bone than tendon ! Reticular Thinner, interwoven, network Resist force in many directions Stabilize positions of organs and vessels against changing positions and gravity Elastic Elastin Wavy Return to position after stretching Socrative 8. list the three types of fibers Loose CT “packing” between organs Cushion and stabilize Three types Areolar Spaces Least specialized Resilient Padding “pinched” skin Adipose Padding Insulation White fat – Brown fat – vascular and lots mitochondria; metabolism Reticular Spleen, liver, lymph nodes Dense CT Mostly fibers Lots of collagenous fibers Divided into dense regular and dense irregular Regular Tendons and ligaments Irregular Surround flat muscles, bones and organs Also found in the cavities of the joints Fluid Connective Tissue Blood Watery, fluid matrix known as plasma Distinct populations of cells (RBC, white and platelets) Dissolved proteins Lymph Forms as interstitial fluid Enters lymphatic vessels Eventually returned to large veins near the heart Process (vessels to interstitial to lymph and back to vessels) is necessary for immunity and homeostasis – blood volume Supporting CT Cartilage Chondrocytes in lacunae with matrix and fibers Three types (pg 129) Hyaline ; stiff but flexible, decrease friction – ribs, joints, larynx, nose Elastic; tolerates distortion – ear, epiglottis Fibrocartilage; resists compression – knee, intervertebral discs Bone Calcium salts make up matrix Collagen fibers Blood vessels with lacunae that contain osteocytes Socrative 9. in fluid CT, like blood, what is considered the ground substance, the fibers and the cells? 10. in supporting CT, like bone, what is considered the ground substance, the fibers and the cells? Membranes Barrier Epithelia + CT 4 types Mucous Membranes Line digestive, respiratory and reproductive Moist, low friction, lubrication Serous Sealed Pericardium, viscera, thin, permeable, constantly diffusing fluids Cutaneous Thicker, waterproof and usually dry Synovial At joints Lubrication between bones at articulations socrative 11. list the 4 types of membranes 12. Rate your understanding of CT… using a scale of 1-10; 10 means you REALLY get it, lower numbers mean you do NOT understand.