The pH Scale
advertisement
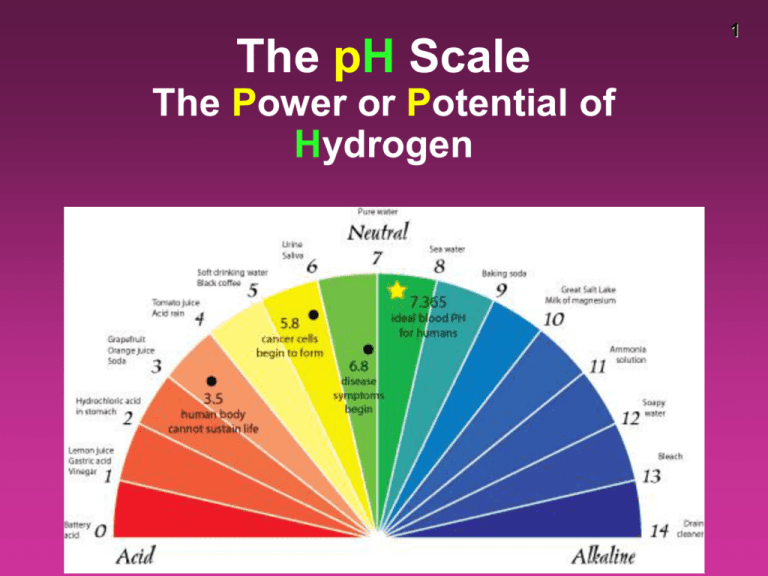
The pH Scale The Power or Potential of Hydrogen 1 2 pH scale • the pH scale is a way of expressing the strength of acids and bases • instead of using very small numbers, we just use the NEGATIVE power of 10 on the Molarity of the H+ ion • under 7 = acid 7 = neutral over 7 = base pH [H+] ions in scientific notation [H+] ions traditionally 0 1x100 1.0 1 1x10-1 0.1 2 1x10-2 0.01 3 1x10-3 0.001 4 1x10-4 0.0001 5 1x10-5 0.00001 6 1x10-6 0.000001 7 1x10-7 0.0000001 8 1x10-8 0.00000001 9 1x10-9 0.000000001 10 1x10-10 0.0000000001 11 1x10-11 0.00000000001 12 1x10-12 0.000000000001 13 1x10-13 0.0000000000001 14 1x10-14 0.00000000000001 3 • pH of 1 is 100x more acidic than pH of 3 • pH of 4 is 1,000x more basic than pH of 1 • pH of 6 is 10,000 less concentrated [H+] than pH of 2 4 Properties of Water 5 • water will self-ionize to a very small extent • in pure water at 25°C, the [concentration] of H+ (or H3O+) and OH- ions are equal – [H+] = [OH-] – both have a concentration of 1.0 x 10-7 M • the ionic product (the [H2O] is considered a constant so left out) constant (Kw) for water at 298 K is: Kw = [H+] [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7 x 1.0 x 10-7 = 1.0 x 10-14 6 • acid solutions have a greater concentration of H+ ions (or H3O+) than OH- ions • basic solutions are opposite and have more OH-, referred to as alkaline solutions when in water pH calculations – Solving for pH pH = - log [H+] [H+] = 10-pH • Example: If [H+] = 1 X 10-10, what is the pH? – pH = - log 1 X 10-10 – pH = - (- 10) – pH = 10 • Example: If [H+] = 1.8 X 10-5 – pH = - log 1.8 X 10-5 – pH = - (- 4.74) – pH = 4.74 7 8 Try These! Find the pH of these: 1) A 0.15 M solution of hydrochloric (HCl) acid – pH = .82 2) A 3.00 X 10-7 M solution of nitric acid (H2NO3) – pH = 6.5 pH calculations – Solving for H+ • If the pH of Coke is 3.12, what is the [H+]? • 10-pH = [H+] • [H+] = 10-3.12 • = 7.6 x 10-4 M 9 10 • A solution has a pH of 8.5. What is the Molarity of hydrogen ions in the solution? pH = - log [H+] 10-8.5 = [H+] 3.16 X 10-9 = [H+] solving for pOH • since acids and bases are opposites, pH and pOH are opposites • pOH does not really exist, but it is useful for changing bases to pH • pOH looks at the perspective of a base pOH = - log [OH-] Since pH and pOH are on opposite ends, pH + pOH = 14 11 12 What is the pH of the 0.0010 M NaOH solution? [OH-] = 0.0010 M pOH = - log 0.0010 pOH = 3 pH = 14 – 3 = 11 13 pH [H+] [OH-] pOH 14 pH testing • There are several ways to test pH –Blue litmus paper (turns red = acid) –Red litmus paper (turns blue = basic) –pH paper (multi-colored) –pH meter (7 is neutral, <7 acid, >7 base) –Universal indicator (multi-colored) –Indicators like phenolphthalein –Natural indicators like red cabbage, radishes 15 16 pH meter • tests the voltage of the electrolyte • converts the voltage to pH • must be calibrated with a buffer solution and stored in a solution pH indicators • indicators are dyes that can be added that will change color in the presence of an acid or base. • some indicators only work in a specific range of pH • once the drops are added, the sample is ruined • some dyes are natural, like radish skin or red cabbage 17