05 Energy in Ecosystems 2
advertisement

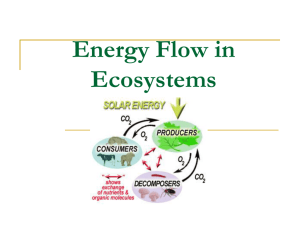
Energy in Ecosystems ALL LIVING THINGS USE ENERGY The earth is SOLAR POWERED! The source of all energy for ecosystems is the Sun. The Sun: 1) lights and warms the surface of the Earth 2) provides energy needed to evaporate water from the oceans and lakes, to form rain and snow 3) provides energy used by green plants to make the compounds that maintain their lives and serve as food for all organisms Of the energy that penetrates into the lower atmosphere, about 30% is reflected by clouds or the Earth’s surface. The remaining 70% warms the surface of the planet, causing water to evaporate, and generating the water cycle and weather. Only a very small portion (about 1%) of the sun’s energy is actually used by green plants for PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Photosynthesis (1:59 min): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LgYPeeABoUs&feature=related Another song (1:52 min): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C1_uez5WX1o&feature=related Photosynthesis process by which green plants use sunlight to produce carbohydrates (glucose/sugars) trap light energy into chemical bonds of sugar AUTOTROPHS = PRODUCERS - make their own food - main producers on land are green plants and in water they are algae About 1% of sunlight is absorbed by primary producers Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 carbon dioxide gas + water + sunlight glucose + oxygen gas Cellular Respiration process plants use to obtain energy from glucose C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy glucose + oxygen gas carbon dioxide gas + water + energy Adv. Cell Resp. song (4:54 min): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3aZrkdzrd04&feature=related Adv. Glucose song (2:45 min): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jJvAL-iiLnQ&feature=fvw Cellular Respiration Plants use the energy released for all the processes inside their cells as well as for growth, repair of tissues and reproduction. Animals also carry out cellular respiration to release the energy but must obtain glucose by eating food containing carbohydrates. - Energy is used for movement, digestion, growth, repair and reproduction. Energy Movement in Ecosystems By categorizing living things by their trophic (feeding) level in their ecosystem, we can better understand how energy flows Energy flows through an ecosystem in a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by being eaten What happens to all the energy in organisms at each level? 90% of the energy is lost at each transfer, most of it as heat Only 10% of the energy that the animal eats is able to be passed on to an animal that eats it We can take a look at this transfer through: Food chains- simple model that shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem Food webs- shows all possible feeding relationships in a community at each trophic level - Represents a network of interconnected food chains Food chains and Energy Song (2:46 min): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TE6wqG4nb3M Calorie definition - a unit of heat equal to the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by one degree at one atmosphere pressure; used by nutritionists to characterize the energy-producing potential in food Food chain (just 1 path of energy) Food web (all possible energy paths) Definitions AUTOTROPHS = PRODUCERS - make own food using photosynthesis HETEROTROPHS = CONSUMERS - get energy from consuming other organisms Other Heterotrophs/Consumers: HERBIVORES – eat only plants CARNIVORES – eat only animals OMNIVORES – eat both plants and animals Other Heterotrophs/Consumers DETRITIVORES – feed on plant and animal remains Examples: mites, earthworms, snails, crabs, vultures DECOMPOSERS – break down and absorb organic matter Examples: bacteria and fungi 4th trophic level 3rd trophic level 2nd trophic level 1st trophic level Energy/Trophic Levels First Trophic level – producers/autotrophs Second Trophic level – primary consumers, herbivores that feed directly on producers Third Trophic level – secondary consumers, primary carnivore that relies directly on primary consumers Fourth Trophic level – tertiary consumers, secondary carnivore that relies directly secondary consumers Keeps going…..