Energy Flow in Ecosystems
advertisement

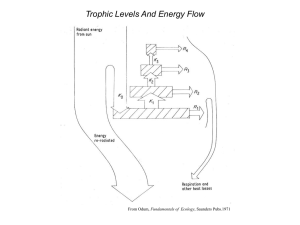
Energy Flow in Ecosystems Food chains: show the path of energy through trophic (feeding) levels Energy come from the Energy is not recycled – it decreases and is “lost” (made unavailable in the form of heat) Level 1 - Producers Undergo photosynthesis (plants, algae, some bacteria) Use energy from the sun to make food (glucose) Level 2 - Primary (1) Consumers Herbivores – eat plants Level 3 – Secondary (2) Consumers Carnivores – eat meat Omnivores – eat both meat and plants Margay Pygmy Golden Headed Lion Tamarin Detritivores - obtain energy from dead organisms at all trophic levels Decomposers – cause decay Bacteria, fungi, worms Rabbit Scavengers – feed on the remains of dead organisms snails, crabs, worms, raccoons, maggots, vultures, hyenas Gecko Review PRACTICE!!! Producer Fourth order (quaternary) consumer Second order (secondary) consumer First order (primary) consumer Third order (tertiary) consumer Food Web vs. Food Chain What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Energy flow through ecosystems can be represented using a pyramid - why? 10% of the energy at each level is passed on to the next level, 90% is used by heat and metabolism. Energy decreases as you move through trophic levels! It takes a lot of vegetation to support higher trophic levels.