The Culture of Sparta
advertisement

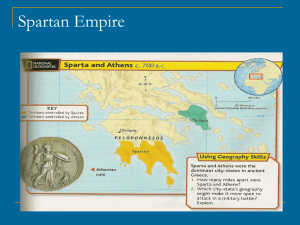
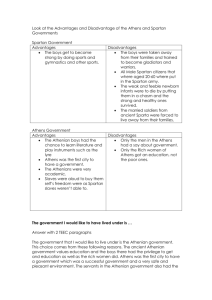
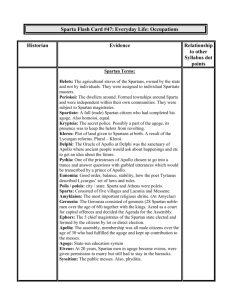
.” To call it a mere barracks bereft of high culture, as did certain Athenian propagandists, was probably going to far- but not all that much too far.” Paul Cartledge Culture can be defined as all the ways of life, arts, beliefs and institutions of a population that are passed down from generation to generation. Culture has been called "the way of life for an entire society." As such, it includes codes of manners, dress, language, religion, rituals, norms of behavior such as law and morality, and systems of belief as well as the art, music and architecture Culture is often embedded and transmitted through stories, whether they are deep and obviously intended as learning devices, or whether they appear more subtly, for example in humor and jokes. Spartan myths such as those of Helen and Menelaus, Leonidas elevated the values of courage and self sacrifice ,state needs over individual needs. Spartan Society from Archaic times to the 4th century cannot be said to be in any way, politically, economically or culturally a static one. Archaeological evidence from such sites as Artemis Orthia and the Meneleon suggest a rich variety of artistic skill using bronze, ivory, terracotta and limestone down to the late 6th century BC. The writing of and appreciation of poetry such as Tyrtaeus, Terpander and Alcman, although profuse in the early period still resonates in the classical 5th and 4th centuries despite the impact of Lycurgan reforms. What can be seen over time, however, is the appropriation and transmission of certain cultural values which supported the norms of a militaristic society. Poetry such as Tyrtaeus which evoked the emotions of courage and self sacrifice became almost iconic, while art and sculpture, still displaying skill became more domestic (bone rather than imported ivory) and utilitarian ( kyliks cups) Cartledge’s opinions provide a freeze frame view and reflects only the devolution of Spartan culture in the 5th and 4th centuries, rather than the rich and varied culture of the 8th, 7th and 6th centuries BC.