Kelly et al 2013 - University of Washington
advertisement

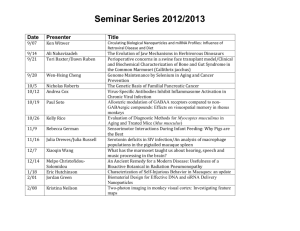
Contributions to SST Anomalies in the Atlantic Ocean [Ocean Control of Air-Sea Heat Fluxes] Kathie Kelly Suzanne Dickinson and LuAnne Thompson University of Washington, Seattle WA USA SST Science Team, Seattle, WA 2013 Applied Physics Laboratory University of Washington Motivation Want to understand origins of low frequency (climate-related) ocean anomalies Kelly et al 2013 Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation • 1st EOF of SST • Tripole structure Kelly et al 2013 Contributions to SST • • • • Surface heating Vertical penetration Upwelling & mixing Horizontal advection/diffusion Kelly et al 2013 Mixed Layer Heat Budget Mixed layer temperature (here interchangeable with SST): ¶T Qnet 2 hp = - ( hpu ) ·ÑT - (T - T- ) we + hpKÑ T ¶t rc p Problems: • Heat penetration hp not mixed layer depth • Time varying hp not known • Advection difficult to compute • Temperature below mixed layer not known • Entrainment velocity unknown Kelly et al 2013 Estimate Mixed Layer Heat Budget • compute climatogical penetration depth by regression with net surface flux (Qnet) • ML advection from surface currents • also Ekman layer advection from wind stress • residual of ML heat budget includes vertical contributions and errors Kelly et al 2013 Estimate Penetration Depth Regress: ¶T Q hc =r ¶t rc p Then hp = rhc Kelly et al 2013 Penetration Depth Ratios Heat penetration deeper than MLD around 20N or 20S Shallower in center of gyres Kelly et al 2013 Compare Advection Estimates Total from OSCAR currents and SST Ekman from wind stress and SST - ( hpu ) ·ÑT Kelly et al 2013 - ( hpu ) ·ÑT ( ) - UE ·ÑT Mixed Layer Heat Budget 40N, 25W Kelly et al 2013 Relative Term Sizes Advection too large particularly in energetic current regions - ( hpu ) ·ÑT Kelly et al 2013 Examine Heat Budget in Tripole Regions • north • middle • south Kelly et al 2013 ML Heat Budget by Region north middle south Kelly et al 2013 SST Versus Heat Content • SST used in most climate studies (bulk flux formulas) • SST decorrelates seasonally, but heat content does not (Deser et al., 2003) • Interannual air-sea interaction depends on heat content (Kelly et al, 2010) T1 T2 T1 T2 H EOFs of SST and Heat Content First mode of SST and heat content similar Heat content from SSH has only 20-year record Kelly et al 2013 Water Column Heat Budget ¶H Qnet 2 = - ò u ·ÑT dz + ò KÑ T dz ¶t rc p where H º ò T dz • No vertical terms • Advection/diffusion estimated as a residual Kelly et al 2013 Compare Heat Budgets Mixed layer ¶T Qnet 2 hp = - ( hpu ) ·ÑT - (T - T- ) we + hpKÑ T ¶t rc p Total column ¶H Qnet = - ò u ·ÑT dz + ò KÑ2T dz ¶t rc p Kelly et al 2013 Heat Content from Altimetric Sea Level Assuming sea level anomalies are primarily from heat content h H = rc p a where η is sea surface height anomaly α coefficient of thermal expansion ρ density of sea water cp heat capacity of sea water Kelly et al 2013 Contributions to Altimetric Sea Level h H = rc p a thermosteric sea level altimetric sea level mass & salinity Kelly et al, J. Climate, accepted Kelly et al 2013 Column Heat Budget by AMO Region north middle south Kelly et al 2013 Meridional Heat Advection Meridional advection heat loss in subtropics Kelly et al 2013, J. Climate, accepted Gulf Stream regions 2 & 3 Summary • Mixed layer budget complicated (vertical distribution of heat in water column) • Mixed layer has large advection terms and large residual (vertical or errors?) • Column heat content budget simple: surface heating vs. advection • EOF 1 (AMO) similar for SST and SSH AMO dominant term is: ML: vertical distribution or errors? Column: advection Kelly et al 2013 Take Home • SST has longest record for computing oceanrelated climate indices • Easier to determine contributions to heat content than to SST • Heat content dominates air-sea interaction on longer (climate) time scales Kelly et al 2013