6th Computer IPOS
advertisement

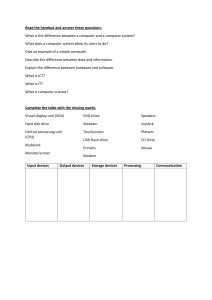
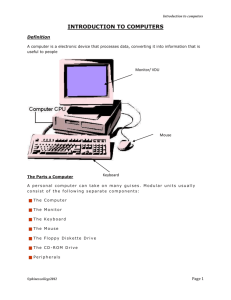
Computer Fundamentals 1 What Is A Computer? An electronic device that receives data, processes data, stores data, and produces a result (output) • Classified by size, speed and application • Uses hardware and software • Comes in different types 2 Hardware The tangible, physical equipment of the computer that can be seen and touched such as: • Computer Case-houses inside components • Monitor-CRT or LCD • Keyboard-contains numbers and letters like a typewriter • Mouse-right click for special functions • Disk Drives-floppy, hard, CD, DVD, Flash • Speakers 3 PARTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM Monitor Speaker Keyboard Computer Case (Processor inside) CD-ROM/DVD Drive Mouse Printer Floppy Disk Drive 4 Input Devices Keyboard Mouse Joystick Touchpad Touch Screen Bar Code Reader Scanner Microphone Digital Cameras 5 Output Devices Monitor: screen that displays information such as text, numbers, and pictures. • Softcopy Printer: gives you information from the computer in printed form. • Hardcopy Speakers: allow you to hear voice, music, and other sounds from your computer. 6 Processing Device Central Processing Unit (CPU)-known as the heart or “brain” of the computer and is responsible for processing the information that has been entered into the computer 7 Which Storage Device Holds The Most Information? Flash, Jump, Thumb Drive CD-ROM DISC 640 MB 1 GB and up DVD DISC 17 GB HARD DRIVES 80 GB and above Terabyte = 1000 GB 8 What Are Peripherals? A peripheral device is one that is attached to a computer in order to expand its ability to perform more tasks Are generally external Some of the more common devices are printers, disk drives, scanners, microphones, speakers, and cameras The devices can be input and output devices Some input devices are: mouse, joystick, keyboard, scanner Some output devices are: monitor, projector, speakers 9 Software The intangible set of instructions that tells the computer what to do; known as programs or software programs. 10 Types of Software Operating System Software • Sets the rules for how computer hardware and application software work together, controls the operation of the computer. • Example: Windows XP, VISTA, Windows 7 Application Software • Lets you accomplish specific tasks based on your needs. • Examples: MS Word, Excel, PowerPoint, MS Works 11 Operating System Software Tasks Boots (starts up) the computer Formats disks Creates folders Saves and retrieves files Moves and copies files Every Computer Has Operating System Software! 12 Application Software Software that works with the operating system to meet a specific need or perform a specific task Examples: MS Word—for word processing documents MS Excel—for math calculation spreadsheets MS PowerPoint—for slide presentations MicroType—for learning to type correctly Internet Explorer—for accessing the Internet 13 Virus/Anti-Virus Software Programs that are written to damage/destroy computers are called viruses. Anti-Virus software has to then be written to prevent (kill) the damage that virus software can do. 14 WHAT DOES IPOS STAND FOR? Input Enters data into the Sends data out of the computerReceives Data Processing Changes data into Output computer Storage Saves for use later usable form 15 How The IPOS Cycle Works INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT STORAGE 16