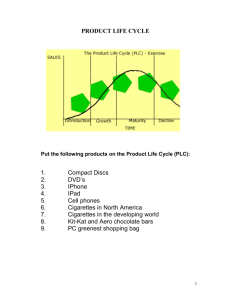
Spring 2011Weekly
advertisement
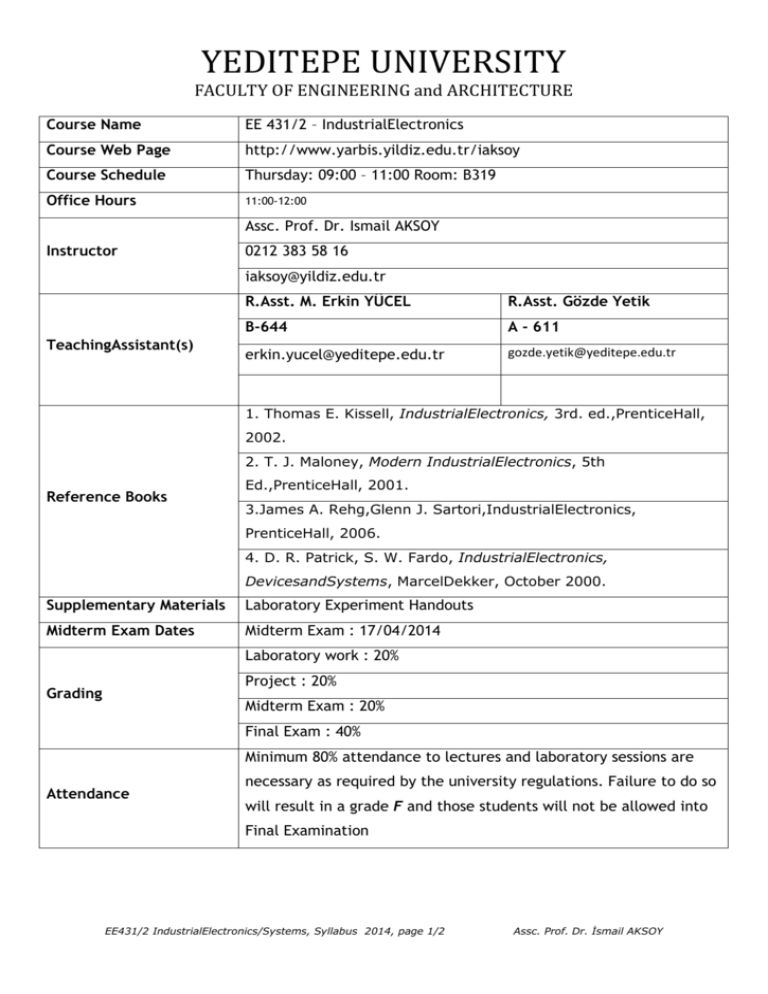
YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING and ARCHITECTURE Course Name EE 431/2 – IndustrialElectronics Course Web Page http://www.yarbis.yildiz.edu.tr/iaksoy Course Schedule Thursday: 09:00 – 11:00 Room: B319 Office Hours 11:00-12:00 Assc. Prof. Dr. Ismail AKSOY Instructor 0212 383 58 16 iaksoy@yildiz.edu.tr TeachingAssistant(s) R.Asst. M. Erkin YÜCEL R.Asst. Gözde Yetik B-644 A - 611 erkin.yucel@yeditepe.edu.tr gozde.yetik@yeditepe.edu.tr 1. Thomas E. Kissell, IndustrialElectronics, 3rd. ed.,PrenticeHall, 2002. 2. T. J. Maloney, Modern IndustrialElectronics, 5th Reference Books Ed.,PrenticeHall, 2001. 3.James A. Rehg,Glenn J. Sartori,IndustrialElectronics, PrenticeHall, 2006. 4. D. R. Patrick, S. W. Fardo, IndustrialElectronics, DevicesandSystems, MarcelDekker, October 2000. Supplementary Materials Laboratory Experiment Handouts Midterm Exam Dates Midterm Exam : 17/04/2014 Laboratory work : 20% Project : 20% Grading Midterm Exam : 20% Final Exam : 40% Minimum 80% attendance to lectures and laboratory sessions are Attendance necessary as required by the university regulations. Failure to do so will result in a grade F and those students will not be allowed into Final Examination EE431/2 IndustrialElectronics/Systems, Syllabus 2014, page 1/2 Assc. Prof. Dr. İsmail AKSOY YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING and ARCHITECTURE Spring 2011Weekly CourseOutline (tentative) 1. Introduction and outline of the course, definition of industrial electronic systems, solidstate devices used to control power: thyristor, triac, power transistor, power mosfet, IGBT, operation principles, voltage-currentcharacteristics, and comparison of power semiconductors. Solid-state devices used for firing circuits. 2. Industrial power supplies: single- and three-phaserectifiers, inductive and capacitive filtering requirements. 3. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): parts of a PLC, timing and counting, relaylogic, ladder logic diagram, PLC programming. 4. PLC continued. 5. AC-AC converters for power control in AC circuits: single- and three-phase AC choppers, phase-control and integral-cycle control techniques. 6. DC-DC converters: Linear vs. switching power supplies, buck, boost and buck-boost converters, isolated flyback, forward, half/full bridge converters. 7. Inverters: single- and three-phase square wave inverters, pulse-width modulation(PWM) control technique. 8. Application of operational amplifiers: instrumentation amplifiers, hysteresiscomparators, integrators, differentiators, and signal generators. 9. Application of operational amplifiers: continued. 10. Open- and closed-loop feedback systems: proportional, integral, and derivative controllers, realization with operational amplifiers, controller tuning (Ziegler-Nichols). 11. Input Devices: Sensors, transducers, and transmitters, temperature, pressure, flow, level, position, speed, motionsensors. 12. Input devices continued. 13. Output devices: valves, relays, contactors, variable frequency drives, DCdrives. 14. Output devices continued. LaboratoryExperiments 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Single-phasefull-wave bridge rectifier and linearregulator. Traffic Light Control System for an Intersectionusing S7-300 PLC Power control in AC circuits using an AC chopper: LampDimmer. Switched-mode DC-DC conversion using buckconverter. Controlling a squirrel-cage induction motor with Simatic S7-300 PLC. Closed-loop temperature control of an electrical heater. Prepare group report for eachexperiment. If no report is submitted, all group members will receive zero grade.Reports must obey the sample report document format given in web page (other wise zero grade from the report). EE431/2 IndustrialElectronics/Systems, Syllabus 2014, page 1/2 Assc. Prof. Dr. İsmail AKSOY