Blood Vessels: The Vascular System
advertisement

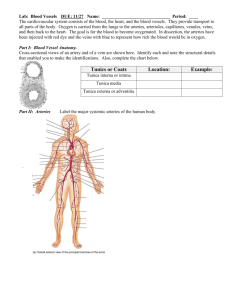
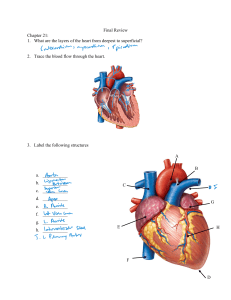
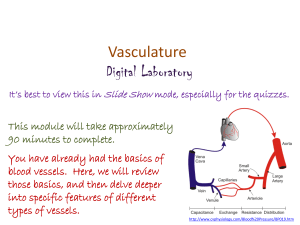
Exercise 21: Anatomy of Blood Vessels 3 Tunics (t. intima, t. media, t. externa) 1 Very thick tunica media in arteries 2 3 Only tunica intima in capillaries Figure 11.9b Blood Vessel Tunic Description Tunica intima • Most internal tunic; • Its smooth surface decreases friction Tunica media Bulky middle tunic contains smooth muscle and elastin; Tunica externa (adventitia) Most superficial tunic *Also called “Tunica adventia” Tunic/ Vessel Tunica Intima Tunica media Tunica externa* Artery X X X Vein X X X Capillary X Only tunica intima in capillaries Capillaries Walls of capillaries are only one cell layer thick to allow for exchanges between blood and tissue Only capillaries directly serve the needs of the body’s cells. It is through the capillary Walls that exchanges are made between tissue cells and blood. Respiratory gases, nutrients, and wastes move along diffusion gradients. Artery Veins VALVE Blood Vessels: The Vascular System Figure 11.9a Elastic recoil of artery propels blood along They have the greatest amount of elastin, enabling them to expand. When the heart relaxes, the recoil propels blood onward. Muscular Pumps aids blood flow in Veins As skeletal muscles surrounding the veins contract and relax, blood is milked through the veins toward the heart. Respiratory Pump aids blood flow in veins! Pressure changes that occur in the thorax during breathing also aid blood return to the heart through the veins. Arteries are thicker than veins Because arteries are closer to the pumping action of the heart, they must be able to expand as blood is propelled into them and then recoil passively as the blood flows off into the circulation during diastole. Arterial walls must be strong and resilient to withstand blood pressure fluctuations.