Introduction to Climates Lesson 4
advertisement

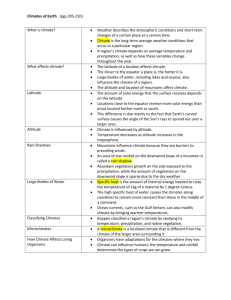
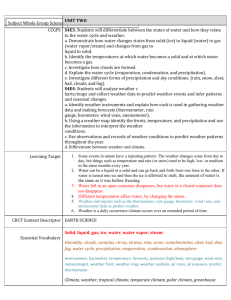
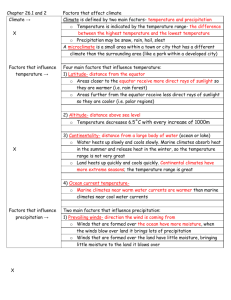
Introduction to Climates UNIT 9 STANDARDS: NCES 2.6.1, 2.6.2, 2.6.4, 2.7.2 LESSON 4 Lesson Objectives In this lesson, you will learn about: – Describe the criteria for classifying climates – Compare and contrast different climates Koeppen Climate Classification According to the Koeppen Climate Classification System, the 5 basic climate types are: Tropical, Dry, Temperate, Cold, and Polar. Tropical Climates To remember a tropical climate, think HOT. Examples are Hawaii, An area is considered tropical if its average coldest month is above 65°F. Some tropical areas are very wet, and some have wet and dry seasons. Vegetation can range from grasses in the drier to tropical rainforests. Tropical Subclimates Within the tropical classification, the seasons are distinguished by the amount of precipitation. There are specific amounts of precipitation that divide the subclimate. Sometimes, an easier way to tell the subclimates apart is by vegetation. Think of vegetation as a clue to the climate of an area. In the tropical climates, the amount of precipitation is a major factor in the vegetation of an area. In some cases of the tropics, the more rain, the more vegetation. Tropical Savanna Tropical savannas sometimes act as a transition zone between the wet tropical rain forest and the dry desserts. The vegetation in tropical savanna areas is usually grasses. Savannas occasionally have scattered trees and shrubs. The tropical savanna has the longest dry season of the tropical climates, where its usual dry season is from December to April. Tropical Monsoon Monsoon climates have dry season, but are known for their long, heavy rainy season. Most monsoon climates are in South Asia. The dry monsoon winds bring cool air from the north, but no moisture. The wet monsoon winds carry moisture from the Indian and Pacific Oceans bringing heavy rains. Tropical Rainforest The tropical rainforest subclimate has the most precipitation of the tropical climates. It rains at least 2.3 inches even in the driest months; it has no dry seasons Tropical rainforests are very close to the equator. They have very lush rainforest vegetation composed of tall, leafy trees. The treetops form a canopy, providing shade for the forest floor. The rainforests are home to thousands of plant and animal species. Dry Climates Think of very little or no rain. Think of Arizona, Idaho or the Sahara Desert. Idaho? Dry climates can be hot or cold. The temperature depends upon altitude and latitude. A portion of Idaho, near Boise, is considered to be a dry climate. A climate is dry if it gets 20 inches of rain or less a year. Vegetation can range from grassland to desert. Dry Climates In dry climates, precipitation is very scarce. When it does rain, the rain evaporates as fast as possible. Most climates that have 20 inches of precipitation or less fall into this category. A dry climate is a place that has an average of 20 inches of rain or less per year. Dry climates are the only climates classified by precipitation. Other climate types are classified by temperature. Dry Climate: Steppe Steppe climates are considered semiarid. This means they receive more rain than the arid desert climate, but not much more. Steppe climates average about 10-20 inches of rain per year. Steppe climates have the short-grass vegetation, known as steppe vegetation. Trees are rare except along riverbanks. Steppes are often a transition zone between desert areas and more humid climates. Dry Climate: Desert Desert climate are considered arid. This means that they average less than 10 inches of rain per year. Desert climates have no wet season. Desert climates have very little or no vegetation. When they do have plant life it survives by: – Requiring little water – Storing Water – Being widely spaced from other vegetation so its roots can absorb water from a large area. – A cactus is one example of desert vegetation. Temperate Climate Most of the world’s population lives in temperate climates because: Most of the land of the world is located in the mid-latitudes. The mid-latitudes are where the temperate climates occur. Many people think of the temperate climate as the “just right” climate. Not “too hot” like the tropics, and not “too cold” like the colder climates. The temperate climates are just right for human comfort and for growing crops that feed large populations. Temperate: Humid Subtropical The entire humid subtropical climate has warm, wet summers. It has hot summer temperatures that average above 71° F. This climate is very close to Tropical Savanna in season and temperature, but is colder and has a wider range of temperatures. Vegetation in the humid subtropical climate is mixed forest and some grasses. Temperate: Marine West Coast The marine west coast climate has wet winter and summer seasons. It also has cool summers, with temperatures averaging below 71° F. The name of the subclimate gives you an idea of its location. This climate is found primarily on the west coasts of continents in midlatitudes. The marine west coast subclimate is farther from the equator than the Mediterranean subclimate, and has coniferous forest vegetation. Cities in the Marine West Coast subclimate are: Edinburgh, Scotland; Bremerhaven, Germany; Salem, Oregon Temperate: Mediterranean Mediterranean areas have wet winters and dry summers. Vegetation in Mediterranean areas is varied. It ranges from scrub to grassland to woodlands. Some people call this kind of vegetation “chaparral”, a Spanish word that means “an area of small evergreen oak trees.” The Mediterranean climate occurs around most of the Mediterranean Sea. Cold Climates Think four seasons. Short growing seasons with frost. Think Vermont and the Northeast. The Cold Climates have four seasons of about the same length. The warmest month average is above 50 ° F and the coldest month average is below 27° F. The precipitation varies. The vegetation is mixed forest or evergreen forest. The cold climate is sometimes called the continental climate because it forms over large continents. Almost no land masses in the Southern Hemisphere are large enough to support this climate. Cold: Humid Continental The humid continental subclimate has year-round precipitation. The other cold climates do not have precipitation all year. It has mixed forests and some grass vegetation. The mixed forests make for a beautiful fall with the changing colors of the leaves. Quebec Canada is an example of humid continental subclimate. Cold: Subarctic The subarctic subclimate has a dry winter season—it receives 10 times more precipitation in the summer than in winter. Subarctic climates have coniferous forest vegetation. Reykjavik, Iceland is not subarctic due to the higher temperatures and year-round rain. However Irkutsk, Russia is subarctic due to temperature and dry winters. Polar Think cold and dry. Think about the poles. Think Alaska or Antarctica. The Polar Climates are cold all year. The average temperature of the warmest month is below 50° F. The polar climates are also dry. The vegetation is mosses and low shrubs or no vegetation at all. Polar: Tundra The tundra subclass of polar climates has precipitation of 5 to 10 inches per year. It supports moss, lichen, and low shrub vegetation. This is sometimes referred to as tundra vegetation. Snow and ice melt for at least part of the year in tundra areas, but the area is called permafrost, since lower layers of the soil remain frozen year-round. Polar: Polar Ice The polar ice subclass has no temperature above 50°F. It averages less than 10 inches of precipitation per year. Since the polar ice cap never melts, this subclass has no vegetation. The North Pole, Alaska is not polar ice due top the temperatures above 50°F, but at the South Pole Station, it is definitely Polar Ice. Section Review 9.4.1 Compare and contrast the five main climates Describe the climate of North Carolina in terms of temperature, rainfall, and vegetation. Of the different types of climates, which do you think would be the most strongly influenced by the jet stream.