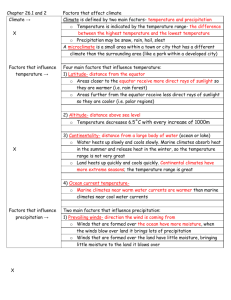
Climates of Earth (pgs.205-210) What is climate? Weather describes
advertisement
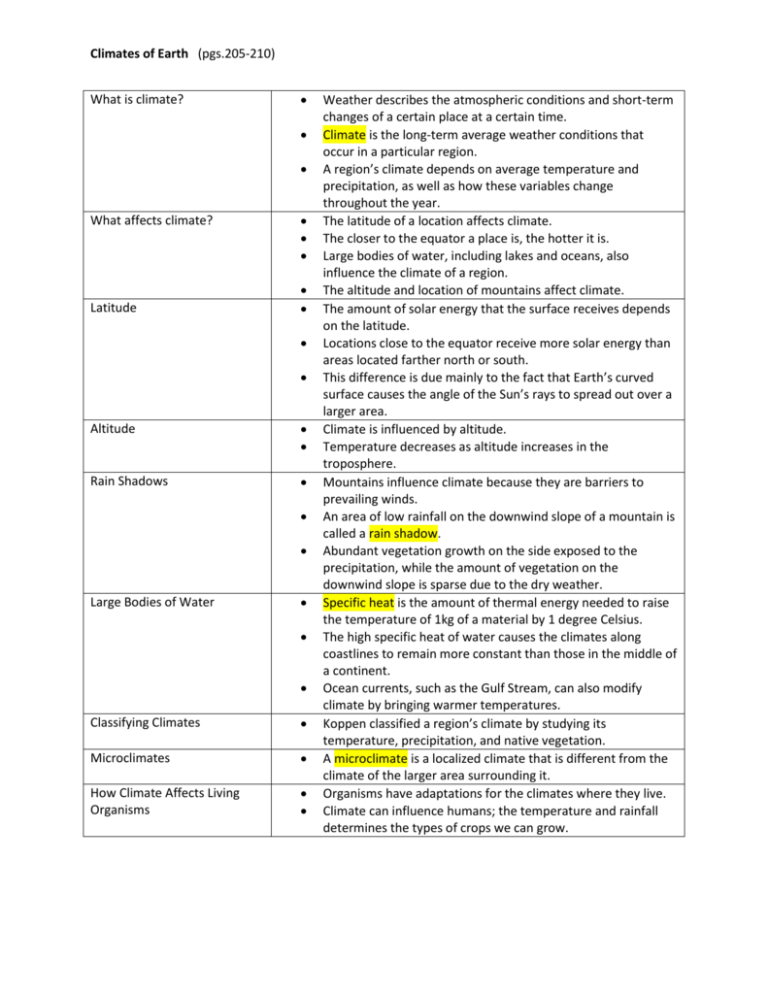
Climates of Earth (pgs.205-210) What is climate? What affects climate? Latitude Altitude Rain Shadows Large Bodies of Water Classifying Climates Microclimates How Climate Affects Living Organisms Weather describes the atmospheric conditions and short-term changes of a certain place at a certain time. Climate is the long-term average weather conditions that occur in a particular region. A region’s climate depends on average temperature and precipitation, as well as how these variables change throughout the year. The latitude of a location affects climate. The closer to the equator a place is, the hotter it is. Large bodies of water, including lakes and oceans, also influence the climate of a region. The altitude and location of mountains affect climate. The amount of solar energy that the surface receives depends on the latitude. Locations close to the equator receive more solar energy than areas located farther north or south. This difference is due mainly to the fact that Earth’s curved surface causes the angle of the Sun’s rays to spread out over a larger area. Climate is influenced by altitude. Temperature decreases as altitude increases in the troposphere. Mountains influence climate because they are barriers to prevailing winds. An area of low rainfall on the downwind slope of a mountain is called a rain shadow. Abundant vegetation growth on the side exposed to the precipitation, while the amount of vegetation on the downwind slope is sparse due to the dry weather. Specific heat is the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a material by 1 degree Celsius. The high specific heat of water causes the climates along coastlines to remain more constant than those in the middle of a continent. Ocean currents, such as the Gulf Stream, can also modify climate by bringing warmer temperatures. Koppen classified a region’s climate by studying its temperature, precipitation, and native vegetation. A microclimate is a localized climate that is different from the climate of the larger area surrounding it. Organisms have adaptations for the climates where they live. Climate can influence humans; the temperature and rainfall determines the types of crops we can grow.