File
advertisement
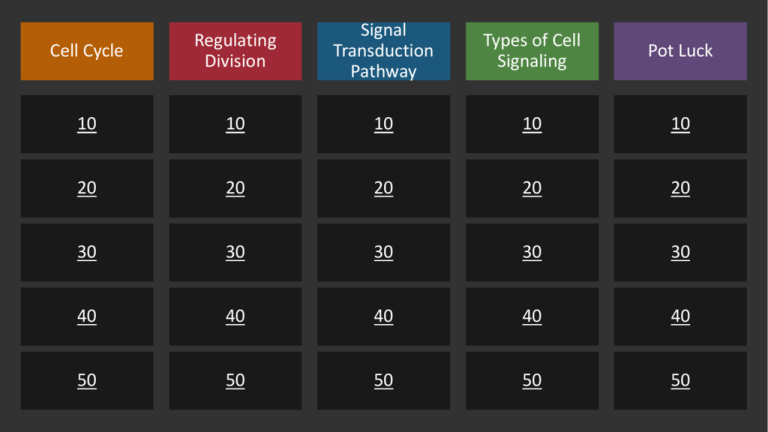
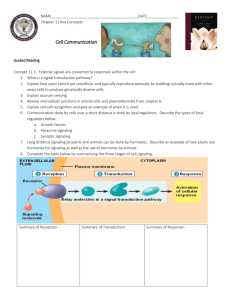
Cell Cycle Regulating Division Signal Transduction Pathway Types of Cell Signaling Pot Luck 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 Category 1 questions follow Question This is the correct order of steps of mitosis. Answer What is prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase (PMAT)? Question This is the longest phase of the cell cycle. Answer What is interphase? Question After cells divide, they re-enter the G1 step to get ready to divide again or they can enter this step to rest. Answer What is G0? Question The “restriction check point” occurs in this part of the cell cycle. Answer What is at the G1 phase? Question When this gene’s functions are turned off, cells begin to pass division checkpoints with damaged DNA which leads to cancer. Answer What is the p53 gene? Category 2 questions follow Question These types of cells will never regenerate if they are damaged. Answer What are muscle and nerve cells? Question The three major checkpoints of the cell cycle occur at these steps. Answer What is G1, G2, and M? Question These cells divide once every 1 to 2 years. Answer What are liver cells? Question These regulatory proteins fluctuate in concentration throughout the cell cycle. Answer What are cyclins? Question This forms when cyclins and cdk’s unite in the cell cycle. Answer What is the MPF complex? (Mitosis Promoting Factor) Category 3 questions follow Question These are the correct steps of the signal transduction pathway. Answer What is reception, transduction, and response? Question A ligand binding to a receptor is very similar to this other analogy in biology because of its specificity. Answer What is a substrate binding to an enzyme? Question When tyrosine kinases are bound by 2 ligands, they join together forming this. Answer What is a dimer? Question These are two examples of steroid hormones that pass easily through the cell membrane to bind to intracellular receptors to initiate a response in the nucleus for transcription. Answer What is testosterone and estrogen? Question This is the type of energy required for G-proteins to function. Answer What is GTP? Category 4 questions follow Question This type of cell signaling involves self-signaling in the same cell. Answer What is autocrine? Question Plant cells are able to perform juxtacrine signaling with other cells through these special features in plant cells. Answer What is a plasmodesmata? Question This type of signaling involves hormones and requires traveling great distances through blood vessels. Answer What is endocrine? Question cAMP, cGMP, calcium ions, and IP3 all have this main similarity. Answer What is being secondary messengers? Question This secondary messenger binds to calcium channels in the endoplasmic reticulum to open the channel. Answer What is IP3? Category 5 questions follow Question These form on the outside of centromeres and allow for spindle fiber attachment. Answer What are kinetochores? Question Crowded cells stop dividing because of this growth factor. Answer What is density-dependent inhibition? Question This term describes the fact that cancer cells may spread to other locations of the body. Answer What is metastasis? Question During telophase/cytokinesis, these are to main differences between plant and animal cells. Answer What are cleavage furrows and cell plates? Question This enzyme is responsible for deactivating protein kinases by removing a phosphate group. Answer What is protein phosphatase?