Learning Guide: Origins of Life
advertisement

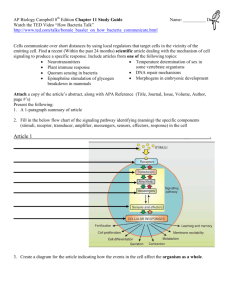
Learning Guide: Cell Communication Bill Activity #24 To Think About: How do cells communicate, transmit and receive chemical signals, and how does signal transmission within and between cells mediate gene expression and cell function? 1st Read About: Cellular Messaging Pg. 206 Campbell’s Biology 9th edition (2-sided column notes) Read the introduction and describe the importance of cell communication and how it is evidence for the the evolutionary relatedness of all life. 2nd Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s video 036 Evolutionary Significance of Cellular Communication video and take notes . 3rd Read About: External signals are converted to responses within the cell Pg. 206-210 Campbell’s Biology 9th edition (2 –sided column notes) o Explain what a signal transduction pathway is and how yeast mating serves as an example of this pathway. o Describe quorum sensing and its importance for bacterial populations. o Local vs. Long Distance Signaling –create two columns in your BILL to take notes on There are two local signaling types: paracrine and synaptic. Explain and give an example for each. Explain long distance signaling/endocrine signaling and give examples. o There are three stages of cell signaling. First describe Sutherland’s work with the hormone epinephrine and how it has lead to the process of cell communication. Create an illustration that shows an overview of cell signaling. Describe the three major steps that occur in this pathway that allow communication to occur. 4th Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s video 037 Cellular Communication video, create the flow chart in your BILL and take notes on it. In this video Mr. Andersen explains analogies between various methods of communication humans use and methods of cell communication. Create an illustration of each type that explains how the human communication method he describes is like a cell communication method. 5th Read About: Reception: A signal molecule binds to a receptor protein, causing it to change shape Pgs. 210-214 Campbell’s Biology 9th edition (2 –sided column notes) o Explain the term ligand and its importance o There are three types of receptors in the plasma membrane. Read and take notes on the three types illustrated on pgs. 211-213. o Describe the key difference between receptor tyrosine kinases and G protein-coupled receptors o There are also intracellular receptors. Read and take notes on this type, pg. 214 Transduction: Cascades of molecular interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell. o Describe two benefits of multistep pathways o Explain why communication pathways regulated by protein kinases act like falling dominoes. o Explain the role of protein kinases and protein phosphatases in transduction o Describe the difference between a first messenger and a second messenger o Two common second messengers are cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium ions (Ca2+). Explain the role of the second messenger cAMP in Figure 11.11 from the text. o Explain the important relationship between the second messenger and protein kinase A. o List three types of pathways often induced by calcium ions. 6th Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s Video and take notes on it (separate page in your BILL). Last:Mr. Andersen’s “Signal Transduction Pathways” video Supplementary Resources: Click the links below for more information to help you learn more about this lesson. McGraw Hill: Membrane-Bound Receptors that Activate G Proteins Learn More: For more information about membrane structure and function, use the links below: Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine, 1994: Alfred Gilman, Martin Rodbell, “for their discovery of G-proteins and the role of these proteins in signal transduction in cells.” Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine, 1998: LouisIgnarro, Robert Furchgott, and FeridMurad, “for their discoveries concerning nitric oxide as a signaling molecule in the cardiovascular system.” Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine, 2000: ArvidCarlsson, Paul Greengard, and Eric Kandel, “for their discoveries concerning signal transduction in the nervous system."