I. Animal Cell Structure - Crestwood Local Schools
advertisement

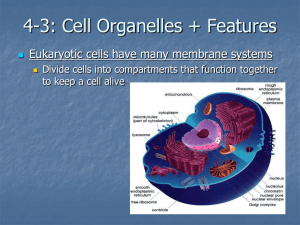
I. Animal Cell Structure A. The cell is the basic unit in the body 1. Consists of a plasma membrane, cytosol, and organelles B. Plasma membrane 1. The plasma membrane surrounds cells and separates from the external environment 2. Composed mostly of a phospholipid bilayer, proteins, with cholesterol a. Proteins are either integral or peripheral 1. Integral proteins are glycoproteins that extend through the bilayer 2. Peripheral proteins are loosely attached to the interior or the exterior of the membrane 3. Considered to be fluid mosaic model with proteins like an iceberg in the ocean C. Cytosol 1. Cytoplasm is the substance inside cell between membrane an nucleus 2. Consists mostly of water with proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and inorganics D. Organelles 1. Specialized structure with certain appearances 2. Nucleus- usually largest, in all but red blood cells, control activities, and house genetic info a. Consists of a membrane, nucleolus, and DNA 3. Ribosomes- spheres of RNA that make protein 4. Endoplasmic reticulum- membrane network through cell that transport and synthesizes molecules, detoxifies, and release a. can be rough or smooth 5. Golgi Apparatus- flat sacs that process, sort, and deliver proteins and lipids 6. Lysosomes- spherical vessicles with digestive enzymes; a lot in white blood cells 7. Mitochondria- many layered organelles used to perform respiration a. Folds or cristae provide surface to make ATP 8. Cytoskeleton- microfilaments and microtubules give support 9. Flagella and cillia- several proteins linked in a tube-like projection for movement 10. Centrioles- paired cylinders used for pulling chromosomes during division