phospholipid bilayer
advertisement

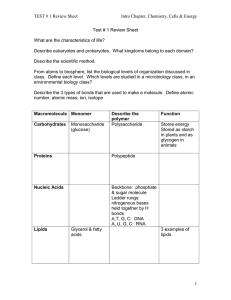
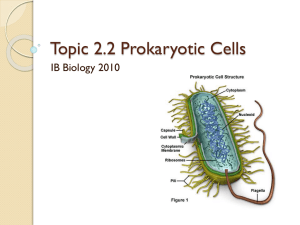
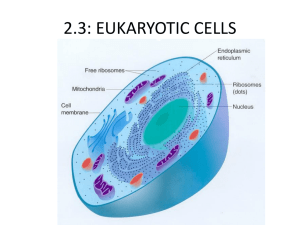
Cellular Structure and Transport Chapter 4 - Intro and section 1 - Explain the significance of compartmentalization of materials in a cell - Why is a cell’s limited? Explain what happens to the surface to volume ration as a cell grows as well as its effect on the viability of the cell. Chapter 4 - Intro and section 1 - Compare and contrast the pros and cons of light and electron microscopy - how can we chemically analyze the structures of a cell - Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of size, structure and complexity Chapter 4 - Intro and section 1 - Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of size, structure and complexity Chapter 4 - section 5 - Describe the structure of the cell wall for plants and bacteria including: structural composition Functions mechanisms by which molecules move through it Chapter 5.1 - Discuss the location and role each of the following play in the plasma membrane - phospholipids - Integral, peripheral, transmembrane proteins - Cholesterol - glycolipids/glycoproteins - Be able to relate the chemical composition of each of the above to their location in the membrane Chapter 5.2 - Differentiate between passive and active transport in terms of energy requirements and concentration gradient - What criteria determine whether a molecule can pass through the phospholipid bilayer using simple diffusion? - How does facilitated diffusion differ? Provide several examples. Chapter 5.2 - differentiate between each of the following: channel protein carrier protein voltage-gated channel ligand gated channel Chapter 5.2 and Chapter 25.3 - In what ways can water move across the membrane? - What do the terms hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic mean and how do they relate to the movement of water? -How is the movement of water influenced by more than solute concentration in plants? -Turgor pressure? Water potential? - How do transpiration and water potential work together to make sure water moves up the xylem of a plant? Chapter 5.3 - How does active transport differ? - under what circumstances would a cell need to use active transport to move a substance? - describe how the sodium potassium pump works Chapter 5.4 - Bulk transport – how do cells use vesicles to move large quantities in and out of the cell phagocytosis pinocytosis receptor mediated endocytosis