The atomic Nucleus & Radioactivity
advertisement
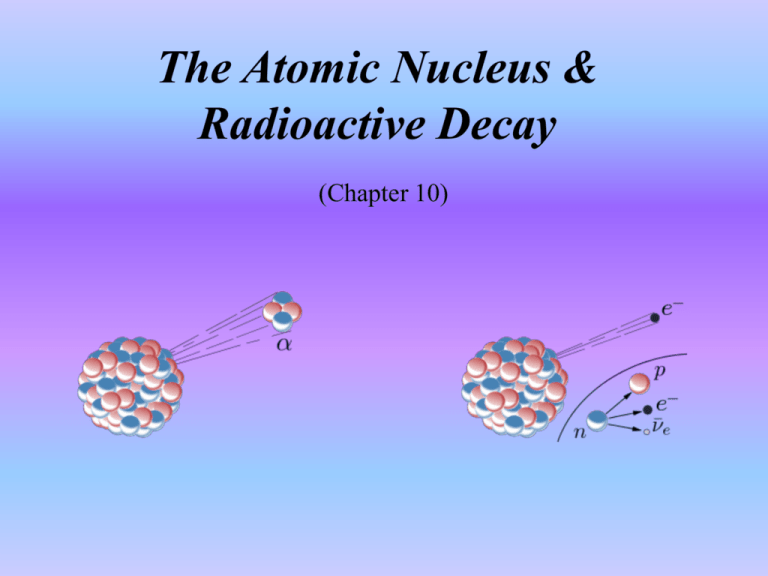
The Atomic Nucleus & Radioactive Decay (Chapter 10) Student Learning Outcomes • Analyze radioactive decay processes • Differentiate between nuclear Fission & Fusion How do we know the number of neutrons? Atomic number = number of protons Mass number = protons + neutrons 17 O−2 8 Practice Classify each atom. Is it an ion? Is it an isotope? 3 He 2 13 6C 34 Cl−1 17 26 Fe 13 6 +1 Li 3 What is the limit for the Strong Nuclear Force? The protons and neutrons in the core of an atom are held together by the strong nuclear force. Diameter < 10-15 m The strong nuclear force balances the electric force in a stable atom. FN FE Nuclear Force vs. Electric Force Strong Nuclear Force Attraction Protons & Neutrons Range < 10-15 m Electric Force Repulsion Protons Range > 10-15 m Practice 1) Would a helium (He) atom or a bismuth (Bi) atom tend to be more unstable? 2) What about a 32He atom? What does radioactivity mean? Radioactivity is the transformation of an unstable atom into a different type of atom. Over 60 radioactive elements can be found in nature. There are 3 general sources of radioactivity. Earth Cosmic Rays Human Produced How do we determine the new isotope? Atoms radioactively decay by emitting high energy particles. XY+a (alpha decay) XY+b (beta decay) XY+g (gamma decay) Alpha radiation: particle (He+) is a positively charged particle that leaves the nucleus. Can cause damage on the surface of matter Beta radiation: (e−) is a negatively charged particle that leaves the nucleus. 8 Li 3 8 Be 4 Beta Particle Can penetrate through several millimeters of matter Gamma Rays: (g) are high energy photons. High Energy Atom No change to nucleus High Energy Gamma Ray released Can pass through all types of matter The Rules Unstable Condition Name Symbol +2 a Neutron/Proton Beta e– –1 Ratio Excited Gamma photon 0 Nucleus b 83+ Protons Alpha 4 2 He+ g The Rules D(Mass #) = – 4 D(Atomic #) = – 2 D(Mass #) = – 0 D(Atomic #) = + 1 No Change Practice Is the atom an isotope? 1. 226 − Ra X + e 88 2. 226 88Ra 3. 222 86Rn X + 4. 14 6C 5. 36 18Ar What makes it unstable? What is the new atom? X + a X + b X + g 4 He 2 What does the half-life of an element indicate? Half-life is the time it takes for one half of an unstable substance to decay into a different substance. Isotope Half Life 15 C 6 14 C 6 2.449 seconds 5,730 years Practice 1. An isotope of radium (Ra) has a half-life of 1620 years. If 1000 grams were placed in a barrel, how much of the material in the barrel would be radium after 6480 years? 2. 22589Ac (Actinium) has a half-life of 10.0 days. How many days would it take to decrease the original amount placed in a barrel to 1/8th of the original amount? What is carbon dating? Carbon dating is the process of using the known half-life of carbon to determine age of a sample. Living plants and animals take in CO2 (Carbon-14) Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope 6C 14 14 7N + b Practice The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. 1. If a piece of wood has 1/2 as much carbon-14 as compared to a living tree, how old is the wood? 2. If a piece of wood has 1/32 as much carbon-14 as compared to a living tree, how old is the wood? A Question to Ponder 3. It is assumed the relative abundance of carbon-14 in our atmosphere has remained constant for the last 50,000 years. How do you think this assumption could affect carbon dating? What is Nuclear Fission? Nuclear fission is splitting apart a nucleus. Electric force wins Nuclear fission is used in atomic bombs & nuclear reactors. Nucleus flies apart Atomic bombs produce a chain reaction. Huge amounts of energy released Nuclear reactors control the rate of fission. A little Uranium yields a lot of energy 8.4 x 1010 Joules per atom A Question Nuclear energy is a clean fuel. It does not pollute the atmosphere. What reasons may people have for not wanting to utilize nuclear energy? What is Nuclear Fusion? Nuclear fusion is the process of forcing atoms together into a new type of atom. Requires very high temperatures and pressures Nuclei must overcome Coulomb Barrier Some mass is converted into energy Nuclear Fusion occurs naturally in stars. Image Credit: NASA 1 Second In The Sun • 1038 Reactions • 600 Billion kg H He • 4 Billion kg Mass Energy • 4 x 1026 Watts http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/astr162/lect/energy/ppchain.html How is radiation measured? Radiation is energy. Lethal doses begin at about 400 – 500 rems The rem: radiation absorbed and the possible biological damage Food Electronics Tobacco Human exposure is about 0.2 rems/year 39 mrems 11 mrems 1,300 – 9,000 mrems