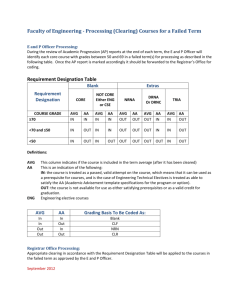
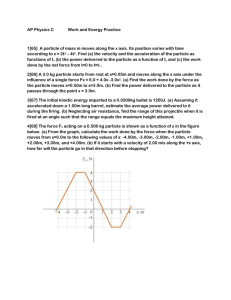
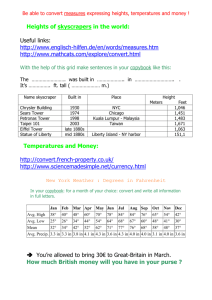
Motion Lab

Motion Lab
Name_________________________ Period______________
Date ____/____/_____
Purpose: To determine how fast something is moving, we need to know the distance the object travels and the amount of time it too to travel that distance. To do this, we will look at 4 different types of motion of members of the class: walking, skipping, running and a slow walk to run. From this data, we will analyze the motion graphically. This graphical analysis will serve as an introduction to the relationships between distance, speed and time.
Procedure:
Timer 1A Timer 2A Timer 3A Timer 4A Timer 5A
Timer 1B Timer 2B Timer 3B Timer 4B Timer 5B
1.
Four (4) members of the group will volunteer/be selected, one each to walk, skip, run and the go from slow walk to fast run.
2.
The walker will begin behind the starting line in order to get to a constant walking speed by the time they reach the starting line.
3.
When the walker gets to the starting line all timers will start their stop watches. Each timer will stop their stopwatch when the walker gets to their particular line.
4.
Each timer should record their time and their partner’s time.
5.
Repeat 2-4 for the skipper, runner, and walk-to-runner
6.
Plot the walking skipping and running data on a single distance-vs-time graph. This will be done by hand first and then on LoggerPro.
7.
Plot the walk-to-run data on another distance-vs-time graph.
8.
Finish the analysis questions.
Position
Walk
Skip
Run
Walk-To-
Run
Analysis
Questions:
Start 0.00m
0.00s
0.00s
0.00s
0.00s
10.00m
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
Show all of your work!
20.00m
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
30.00m
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
1.
What benefit is there to averaging two times for each distance interval?
2.
What are the units of the slope of any of the graphed lines?
40.00m
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
50.00m
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
A:
B:
Avg:
Answer ________________
3.
What is the speed of the walker?
4.
What is the speed of the skipper?
Answer ________________
5.
What is the speed of the runner?
Answer ________________
Answer ________________
6.
Write a general equation from the graph for the runner relating velocity, distance and time. Then determine the distance that would be traveled in the miles after 1.0 hours of this motion.
7.
What is the average speed of the non-uniform motion (aka walk-to-run)?
8.
What kind of motion is described by data that plots as a straight line?
Answer ________________
9.
What kind of motion is described by data that plots as a curved line?
Walk-To-Run
Average
Speed
Time
Midpoints
10.
Using the walk-to-run distance-vs-time graph, determine the instantaneous speed at 3 different times. This information can be found by finding the slope of the tangent line to the graph at these points.
Speed 1 _________________ Speed 2 _________________ Speed 3 _________________
11.
Determine the average speed over each interval for the accelerating motion. Keep in mind that the average speed over each interval is the interval distance divided by the interval time. Place the results of your work in the table below.
0.00 – 10.00m 10.00 – 20.00m 20.00 – 30.00m 30.00 – 40.00m 40.00 – 50.00m
12.
From the data above, construct a speed-vs-time graph, assuming that the average interval speeds actually occur at the time midpoints of each interval. Scale your graph appropriately.
13.
Can you reasonably construct a best fit straight-line for through the data of the speed-vs-time graph? If so, go for it. Again, this should be done by hand first and then on LoggerPro. What are the units of the slope of the line? What is the significance of these units?
14.
What is the slope of the speed-vs-time graph?
Answer ________________