D2C_Topic_1_measure_shapes_formulas
advertisement
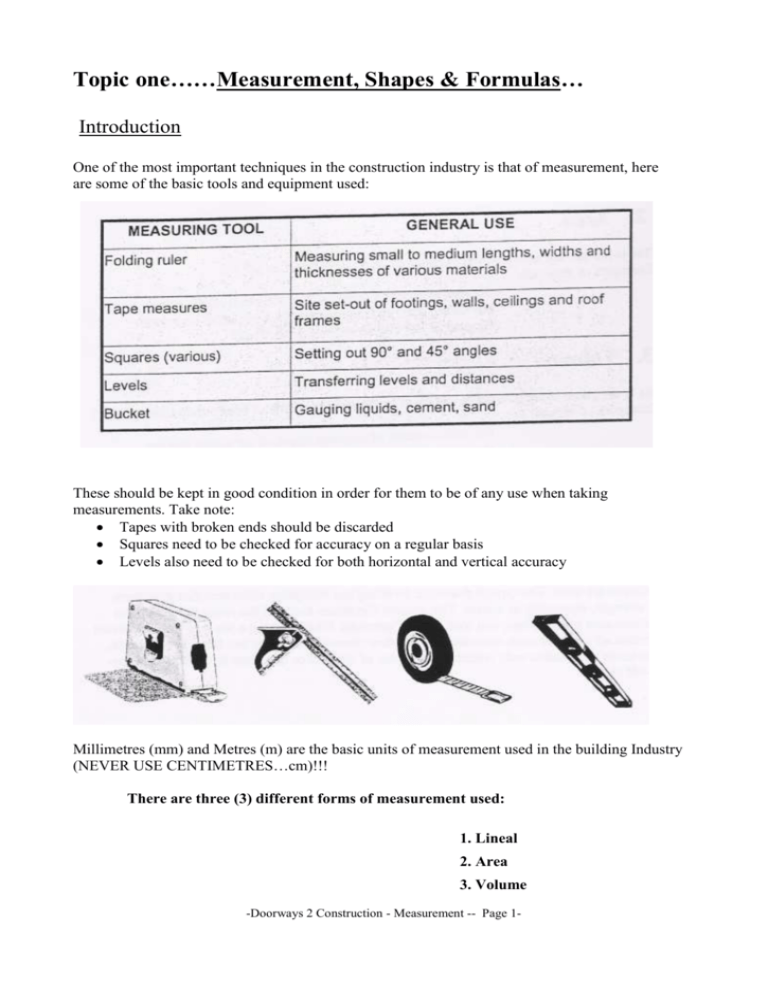
Topic one……Measurement, Shapes & Formulas… Introduction One of the most important techniques in the construction industry is that of measurement, here are some of the basic tools and equipment used: These should be kept in good condition in order for them to be of any use when taking measurements. Take note: Tapes with broken ends should be discarded Squares need to be checked for accuracy on a regular basis Levels also need to be checked for both horizontal and vertical accuracy Millimetres (mm) and Metres (m) are the basic units of measurement used in the building Industry (NEVER USE CENTIMETRES…cm)!!! There are three (3) different forms of measurement used: 1. Lineal 2. Area 3. Volume -Doorways 2 Construction - Measurement -- Page 1- 1. Lineal This is the perimeter or length measurement in running/lineal metres. (Identified as lm.) Examples of linear measurements are: the length of concrete kerbing required around a carpark. the length of timber skirting around a room. the length of plasterboard cornice mould around a ceiling. etc… 2. Area This is the surface area covered in square metres. (Identified as m2) Examples of areas are: the area in metres square (m2) of a concrete floor slab. the area in (m2) of brick paving for an external courtyard. the area in (m2) of tiles to cover the floor. 3. Volume This is the cubic content of space occupied by the length x width x depth. (Identified as m3) Examples of volume are: the cubic content of concrete required for a strip footing. the cubic content of earth required to excavate a sloping site. the cubic content of composition mortar required to lay 1,000 bricks. Usefull Tips!!! The majority of buildings are either rectangular or square. However triangular, circular and other shapes are used. The typical domestic dwelling has triangular structures that give them added strength, especially in trusses. The ancient Egyptians knew of the strength of triangles many thousands of years ago, just look at the Pyramids! When costing a job it is very important to calculate all material costs accurately so we don’t have too much or too little. For instance, did you know that timber only comes in multiples of 300mm or that there is usually 15% loss due to off cuts ! ….O.K. now lets try a few typical workplace exercises !!! -Doorways 2 Construction - Measurement - Page 2- Exercises: Calculate the lineal metres (lm) of skirting required for the following room sizes 1. 6.00m 5.00m 5.00m 11.00m 8.00m 2. 6.00m 3.00m 15.00m 6.00m 9.00m 6.00m 3. Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 950mm. Note: Circumference = Pi x Diameter = D where = 3.14 and D = 2 x radius 950 mm -Doorways 2 Construction - Measurement - Page 3- Exercises: 4. Find the area of a circular swimming pool, with a surface radius of 25m 25m Swimming pool 5. Find the total floor area of the entertainment area below. 25m 12.5m Entertainment Area 60m 14m 6. Concrete Path 10m 14m 10m Garden bed -Doorways 2 Construction - Measurement - Page 4- Exercises: 7. How many cubic metres (m3) of concrete are required to fill a cylindrical column with a radius of 500 mm and a height of 5 m? (make a sketch first) Volume of a cylinder = r2H 8. -Doorways 2 Construction - Measurement - Page 5-