mine safety- learning from industries
advertisement

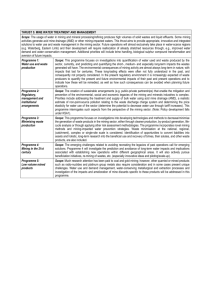
MINE SAFETY- LEARNING FROM INDUSTRIES Management of Mine Safety in India • Governed by Prescriptive Legislation • DGMS – Regulatory Authority as per statute • Indian mining law has strong legislation base, which has evolved over a period of more than one hundred years • Way forward is the system of Self – regulation based on hazard identifications and risk assessments Evolution of safety legislation in india • 1890 - International Labour Conference in Berlin for improvement in the working conditions of miners – 1st trigger for mine statute in India • 1895 – GOI initiated 1st step to frame legislation for mine inspection • 1901 – The 1st Mine Act – enacted • 1923 – The Mines Act 1923 – superseded earlier Act • 1952 - The Mines Act 1952 – superseded earlier Act • 2010 – Bill for amendment of the Mine Act -1952 placed before Rajya Sabha – under scrutiny of Standing Committee of Labour Improvement in safety in CIL 10 years average fatalities 170 180 147 160 140 100 80 103 Fatalities 120 77 60 40 20 0 Av fatalities 1400 1975-84 1985-94 1995-04 2005-11# 170 147 103 77 1172 Av. Serious Injuries Av.Serious Injuries 1200 1000 800 565 600 520 322 400 200 0 Av. Serious Injuries 1975-84 1985-94 1995-04 2005-11# 1172 565 520 322 Improvement in safety in CIL Over the years the safety performance in CIL has been improved and it is attributed to the following reasons: • Collectively commitment shown by the management, workers and regulators • Technological advances in the field of mining methods and use of safer mining machineries. • Continuous improvement knowledge and skill of our workforce through imparting quality training and conscientious safety awareness drive • Strong oversight and assistances from various quarters Challenges Ahead • To solve problems related to increasing depth • To Solve Strata Control problems of deeper UG coal mines. • To solve problems related to ventilation of deeper UG Coal Mines • To Provide apt solutions for Mine Environment Monitoring • To Solve Problems of Dump Slope Stability • To Provide adequate infrastructure for operation and maintenance of Large Capacity HEMM Challenges Ahead • To Create Compatible infrastructure such as standard all weather haul roads in Opencast Mines • To Monitor and Control Mass Blasting and Ground Vibration Problems • To install system for Dust & Noise monitoring • To Prepare and Implement a requirement based Training and HR Capacity Building Plan • To Provide for an effective Emergency Response Mechanism at Mines Suggested thrust area for UG Mining • All new virgin underground mines are to be planned with high degree of mechanization • Large scale introduction of mass production technologies like long wall mining technology, continuous mining technology etc. • Non mechanized existing mines to be quickly converted to mechanized mines through adoption of SDL/LHD and mechanized drilling for roof bolting Suggested thrust area for UG Mining • Scientific strata and environment monitoring; • Risk assessment and mitigation plans; • Faster development of infrastructure for UG minesMechanized shaft and incline drivages • Introduction of quick setting foam stopping for isolating fire • Introduction of notch cutter for speedy recess cutting for construction of sectionalization & isolation stooping • Digitization of mine plan Suggested thrust area for UG Mining • Introduction of man riding systems in large UG mines where travelling is arduous • Adoption of telecommunications in UG mines • Air-conditioning systems for mine ventilation, particularly the deep mines of more than 400m depth or where temperature can not be brought down to 30 degree Celsius with conventional ventilation system • Creation of machinery manufacturing facilities to support UG mechanization Suggested thrust area for OC Mining LIMITING FACTORS OF OC PLANNING • Apart from macro-economic factors including business environment – – – – Depth of reserves Stripping Ratio Extent of surface Area / lands for coal mining Surface constraints including diversion of forest land – Availability of land for dumping Suggested thrust area for OC Mining FUTURE OC MINING • Deep opencast mining • Extending and deepening existing OC mines • Use of more number of surface miner for Coal as well as OB removal • Use of more higher capacity of HEMM • High wall mining to access exposed coal resources in final opencast batters & thin coal seams Suggested thrust area for OC Mining THRUST AREA OF OC MINING • Conservation of reserves- designing of large size pits and amalgamation of adjacent mines for extracting locked up coal in batters and barriers; • Scientific approach for designing pit slopes and dump slopes with appropriate monitoring measures; • Large scale adoption of in pit crushing and conveying of coal and OB Suggested thrust area for OC Mining THRUST AREA OF OC MINING • Standardization of HEMM for various pit capacities • Land reclamation and mine closure plans with monitoring mechanism • Application of IT for traffic management, inventory, maintenance and safety such as GPS based OITDS Experience learned from recent mine disaster ANJAN HILL DISASTER – 06.05.10, Fatalities - 14 • Probable cause - Firedamp explosion caused by spontaneous heating of coal • Lesson learnt – developed potholes to be filled at the earliest – Never allow coal dust to be accumulated in UG – Regular inspection of surface over depillerd areas for early detection of cracks & potholes – special attention to be paid in case of hilly terrain – Continuous monitoring of mine environment where early sign of heating is detected Thank you