Flowers/Reproduction - Ms Kim's Biology Class
advertisement

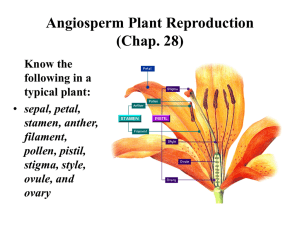
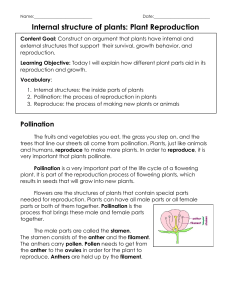
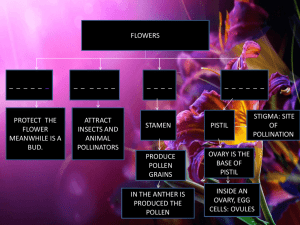
Bellringer-October 1, 2014 Write under exit slip 1) How do flowers reproduce? 2) Do flowers have separate male and female organs? 3) How do monocot and eudicot flowers differ? Flowers/Reproduction Aquaponics Flower • Sexual reproductive structure • Produces egg and sperm • Fertilization takes place inside the flower The flower: the defining structure of angiosperms Reproductive structure: pollen transfer; specialized shoot with modified leaves Sepals: enclose flower before it opens Petals: attract pollinators Stamens: male sex organs; anther (produces pollen), filament Carpels or Pistil: female sex organs; includes stigma, style, ovary, ovules Female reproductive organ Pistil or Carpel *Stigma –top of the pistil, Sticky surface for pollen to stick to *Style – connects the stigma to the ovary *Ovary –contains ovules ( eggs) Male reproductive organ Stamen *Anther – produces sperm nuclei by meiosis. Sperm nuclei are enclosed by pollen grains. *Filament – holds the anther up Pollination • Flowers/fruits can be carried by wind, water, or animals to new locations, enhancing seed dispersal (a) Wings enable maple fruits to be easily carried by the wind. (b) Seeds within berries and other edible fruits are often dispersed in animal feces. Figure 30.9a–c (c) The barbs of cockleburs facilitate seed dispersal by allowing the fruits to “hitchhike” on animals. Pollination: Transfer of mature pollen grains from the anther to the stigma • When a pollen grain lands on the stigma, it germinates and a pollen tube grows down through the style to an ovule (egg) Fertilization • The sperm travels through the pollen tube to the ovule. The sperm & egg fuse forming the zygote (fertilized egg) –this grows into the plant embryo (cells grow by mitosis) *Self pollination –pollen from same flower *Cross pollination – pollen from a different flower - more variation • The ovary and zygote (fertilized ovule) develop and ripen. *The ovule forms the seed and the ovary forms the fruit. • A fruit is a ripened ovary Fruits • Form when ovary with ovules (eggs) ripens • May be dry and hardened (nuts) • May be enlarged and fleshy (berries, apples, tomatoes) …TASTY!!! • Used to help disperse seeds