Monocots vs. Dicots
advertisement

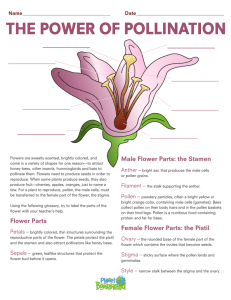
Flowers, Monocots and Dicots Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. identify the parts of flowers 2. identify monocots and dicots 1 2 1 2 1&2 Monocots vs. Dicots FLOWER DISSECTION Lily A B D C Lily B C A Style Stigma Ovary A C B Anther Stamen Filament Stamens and Pistil A B F E C D P S S P P S P = Petal; S= Sepal A B Sepals Bud bract stamens pistil petals sepals FUNCTIONS OF FLOWER STRUCTURES Functions of flower structures Sepal • Sepals- protects the flower while it is a bud Petals • Sepals- protects the flower while it is a bud • Petals- attract insects and animals to aid in pollination Stamen A C B What’s that? • Sepals- protects the flower while it is a bud • Petals- attract insects and animals to aid in pollination • Stamens- male part of the flower which includes the anther and filament; it produces pollen. Anther • Sepals- protects the flower while it is a bud • Petals- attract insects and animals to aid in pollination • Stamens- male part of the flower which includes the anther and filament; it produces pollen. • Anther- produce and release pollen to the stigma of the same or another flower for reproduction. Anther Stamen Filament • Anther- produce and release pollen to the stigma of the same or another flower for reproduction. • Filament- elevates the anther away from the flower for pollen dispersal and transports nutrients to the anther. • Pollen- contains sperm for fertilization. Pistil • Anther- produce and release pollen to the stigma of the same or another flower for reproduction. • Filament- elevates the anther away from the flower for pollen dispersal and transports nutrients to the anther. • Pollen- contains sperm for fertilization. • Pistil (Carpel)-female part of the flower which includes the stigma, style and ovary; it produces ovules, which are similar to eggs in animals. Produces seeds and fruit. Stigma • Anther- produce and release pollen to the stigma of the same or another flower for reproduction. • Filament- elevates the anther away from the flower for pollen dispersal and transports nutrients to the anther. • Pollen- contains sperm for fertilization. • Pistil (Carpel)-female part of the flower which includes the stigma, style and ovary; it produces ovules, which are similar to eggs in animals. Produces seeds and fruit. • Stigma- collects pollen on its surface and aids in fertilization B C A Style Stigma Ovary Style A Where is it located? B C What does it do? Style A Where is it located? Style C What does it do? • Pollen- contains sperm for fertilization. • Pistil (Carpel)-female part of the flower which includes the stigma, style and ovary; it produces ovules, which are similar to eggs in animals. Produces seeds and fruit. • Stigma- collects pollen on its surface and aids in fertilization • Style- elevates the stigma to collect pollen A Ovary Where is it located? B What does it do? C A Ovary Where is it located? B What does it do? Ovary • Pollen- contains sperm for fertilization. • Pistil (Carpel)-female part of the flower which includes the stigma, style and ovary; it produces ovules, which are similar to eggs in animals. Produces seeds and fruit. • Stigma- collects pollen on its surface and aids in fertilization • Style- elevates the stigma to collect pollen • Ovary- produce ovules (eggs); when fertilized ovules become seeds and fruits. Monocot Dicot FLOWER PARTS Multiples of 3 Multiples of 4 or 5 Dicot Monocot LEAVES Parallel leaf venation Net-like leaf venation Monocot Dicot ROOTS Diffuse Root Taproot STOP HERE! FERTILIZATION A Fruit Development A B Fruit Examples with only 1 seed 1 2 3 4 7 6 5 Example of fruit with multiple seeds Hibiscus F A E B D C Anther Stigma Filament Style Sepal Petals B A Stigmas Pistil & Stamens Anther Underside of Hibiscus Petal Sepal