Structures of the Hydrosphere Study Guide
advertisement

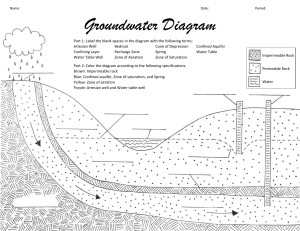
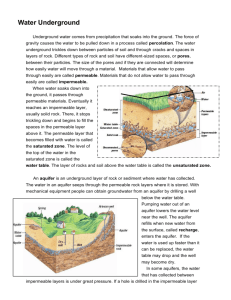
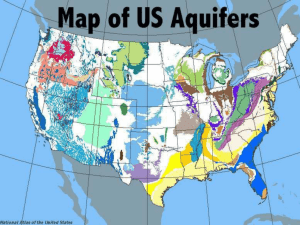
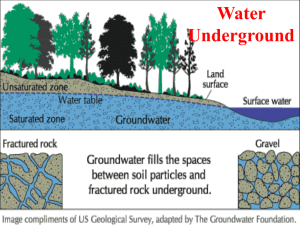
Name: ________________________________________ Date: _________________ Block: ______ Structures of the Hydrosphere Study Guide Please make sure you use this study guide as practice to help prepare for your test. In order to properly study you should also be reviewing: Molecule Journey, Hydrosphere Notes, Water Vocabulary, and Properties of Water Notes 1. Draw and label a water molecule. 2. What is polarity? What does polarity allow water to do? 3. What is surface tenstion? Adhesion? Cohesion? Specific heat? Capillary action? 4. Why is water called the universal solvent? 5. Water is the only substance on Earth that naturally exists in all three states (solid, liquid, gas). Draw a molecular diagram of water in all three states. 6. Where does most evaporation occur and most precipitation fall? 7. How do plants use water? 8. Approximately what percentage of Earth’s water is salt water? 9. Why are wetlands important? Explain three major benefits. 10. What is groundwater? 11. Why is Earth refered to as the “water planet” or the “blue planet”? 12. If an object floats, what is the volume of displaced water equal to? 13. What is a river system made up of? 14. What are watersheds? Tributaies? Divides? 15. How are ponds, lakes and rivers similar? Different? 16. What is the difference between a reservoir and a dam? 17. When water fills a submarine’s flotation tanks, what would happen to the overall density of the submarine? 18. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated? 19. What is the difference between permeable and impermeable? 20. What is transpiration? 21. What is an aquifer? 22. A plastic block floats between a layer of water, which has a density of 1.00 g/cm3, and a layer of glycerin, which has a density of 1.5 g/cm3. What is the possible range for the density of the plastic used to make the block? 23. A rock is gently lowered into a large container that is completely filled with water. The rock is then released. The water that the partially submerged rock displaces is caught in a cup and weighed. What do we know about the weight of the displaced water and the weight of the rock? 24. An object will stay afloat as long as the buoyant force is _____________________________ the object’s weight. 25. What is the density of water? If an object with a density of 0.8 g/mL is placed in water will it sink or float? 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Label and explain the missing sections. How does water enter the area marked with an A? What are the ways in which water can return to Earth’s surface from the atmosphere? Which steps in the diagram involve a change of state? Name a possible path a raindrop falling on the hillside might take to reach the ocean. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. Which well(s) end(s) in a saturated zone? Unsaturated zone? Which well(s) will provide water? Describe how water enters Aquifer A. Are the aquifers permeable or impermeable? Which aquifer would produce an artesian well? Why?