499Martin-JohnEUdev07
advertisement

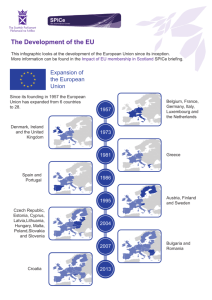
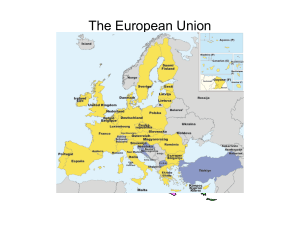
The History and Development of the European Union, Since 1951 By John Martin, 2007 European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) • • • • Treaty of Paris (1951) 6 member organization Franco-German relationship Increased economic production by combining coal and steel resources Leadership and Foresight • Robert Schuman • European integration and cooperation • Jean Monnet (1952-1955) • Post-war debt relief ECSC Institutions • Common Assembly/European Parliament • Council of Ministers • High Authority/European Commission (Schuman) • Court of Justice Treaty of Rome (1957) • European Economic Community (EEC) • Common market (the Six) • European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) • Nuclear energy Merger Treaty (1965) • European Communities (ECSC, EEC, and Euratom) • Joint budget and distribution of power • European Parliament (1962) and budgetary control (1975) Enlargement and Improvement • 1973- change in French presidency and 3 new additions • European Parliament (1979) • 1980’s- southwest Europe (3 more countries incorporated into European Communities) Economic Progress • Schengen Agreement (1985)- borders and police cooperation • 5 out of 12 members • British mainland (Common Travel Area) Single European Act (1986) • Internal market • Qualified majority voting (QMV) • European Council (policy) • Introduction of symbolic flag Economic and Political Unity • German reunification • Maastricht Treaty (1992)- European Union (EU) • 3 nations succeed to EU • Copenhagen European Council (1993) • Amsterdam Treaty (1995) Maastricht Uncovered • Treaty on European Union • Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) • Justice and Home Affairs (JHA) • Eurocorps (5 members) • Trilateral organization of power 21st Century Updates • Treaty of Nice (2001) • Globalization • Coinage and adoption European Integration • • • • 10 members included East meets west Economic disparity and uncertainty 27 total nations Modern EU Politics and Governance • Members of Parliament (MEPs) and political parties • EPP-ED and PES • Regulations, directives, and decisions • Bilateral power distribution (legislative and judicial) Recent Trends and Statistics • Economic diversity and success • Exports and imports • Continental integration and disadvantages • Global involvement Global Impact • • • • Humanitarian aid Environmental focus International competition Positive EU/U.S. relationship EU Problems and Conflicts • • • • • European Constitution (2004) Franco-German supremacy Decreasing EU/China relationship British skepticism New candidate countries Conclusion • Stabilizing Europe with a common market • Uniting east and west • Worldwide responsibility and assistance • Future of the EU Further Reading • Chryssochoou, Dimitris N. 1998. Democracy in the European Union. London. • Kostlowski, Dean J., ed. 2000. The European Union: From Jean Monnet to the Euro. Ohio. • Newman, Michael. 1996. Democracy, Sovereignty, and the European Union. New York. • Wallace, Helen and William Wallace, eds. 2000. Policy-Making in the European Union. Oxford.