Chapter 10 - Banking Notes
advertisement

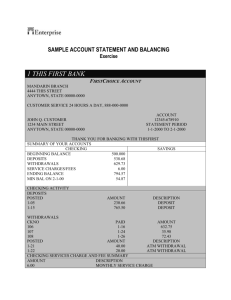
Chapter 7 Banking Essential Questions How does a bank benefit you now? How do you think you will use a bank in the future? If banks didn’t exist, how do you think your life would be different? The Role Banks Play Banks are profit driven private businesses They work to earn a profit by selling financial services Loans – make profit on interest Deposits – invest in open market Investment services How Do Banks Make $$$$? Most income that banks earn comes from the interest they charge when they lend money Example: Suppose you deposit $100 in your bank account. The bank pays you 2% interest to use your money. The bank lends your $100 to a business and charges 6% interest. The banks income is the 4% difference. Banks Provide Security Purchasing power – interest received from savings offset inflation Bank Regulation – Banks are subject to a very high level of government regulation (must maintain certain level of cash) Deposits are Insured – Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) a federal government agency that insures deposits up to $250,000) Banks Simplify Borrowing Banks help people pay for their most important possessions. House / Cars / Education. Businesses borrow for equipment / expansion & start-up costs. Homework Chapter 10 Review Questions (1-17) Types of Banks 1. 2. 3. Commercial Banks Provide many services (FDIC) Focus on savings accounts and loans on property (Home Equity Loan) Savings Banks Savings and Loan Associations 4. Primarily set up to lend money for home mortgages but do offer other services – checking / credit cards / etc. Credit Unions Not-for-Profit for union members – owned by members Higher interest rates on deposits & lower on loans Checking Accounts Checking accounts allow depositors to write checks to make payments A check is a written order to pay a specific payee Checking accounts may also be called a demand deposit account (DDA) Once you write a check and the payee cashes it is “cleared” Until it is cashed it is considered “outstanding” Checking Account Types: Interest-Bearing Checking Accounts – usually large minimums for balance. You can collect interest on your checking account. Noninterest-Bearing Checking – most checking accounts that you do not have to keep a large balance. Why Use A Checking Account? Safety – greatest advantage only the person who the check is made out to can cash it Convenience –large payments – no need to carry around large sums of cash – access to ATM’s Budgeting – Records of your transaction – checks & statements automatically serve as records Credit rating – the first way to establish credit Establish banking relationship – easier to obtain loans, and other services Checking Account Responsibilities Maintain sufficient funds – no overdrafts Keep careful / accurate records (register) Reconcile your account each month Never “postdate” or “float” checks Purposely writing a bad check is a felony Famous Felons TERMINOLOGY Account Balance – the total amount in the account at a specific date Overdrawing – writing a check for more than you have in your account. (NSF Fee) Third Party Check – when you receive a check made out to you, you sign it over to someone else Opening a Checking Account Very Easy – must be 18 years old 2 forms of identification needed Signature Authorization (signature card) Sign your check the same way that you sign signature card Checks can be purchased at bank Check Writing / Parts of a Check Always use Ink Write Legibly Sign exactly as signature card If you make a mistake – “Void” the check & keep it for your records Make sure there is $$ in the account Deposits A Deposit Form must be completed (forms in checkbook or at bank) Endorse checks before depositing them Record the deposit promptly in register Money may not be available until it “clears the bank” Endorsing Checks Signing the back of a check acknowledging you have received the money Checks must be endorsed to be cashed / deposited or transferred Blank Endorsement – just signature Endorsement in Full or Special Endorsement – “Pay to the Order of ___” Restrictive Endorsement – “For Deposit Only” Check Register Booklet provided by your bank for recording all checking account transactions Record all transactions promptly: Deposits Interest Checks (record check numbers) Debits Withdrawals Bank Fees Keep a running account balance at all times Reconciling (Balancing) A Checking Account Bank Statement – at the end of the month the bank will send a statement showing all transactions for the month Balancing (reconciling) a checking account – comparing a check register with the bank statement Statements & Checkbooks Statement Column Balance from statement List deposits not on statement Total statement balance and deposits List checks not on statement Statement balance Checkbook Column Balance from checkbook List deposits not in checkbook Total checkbook balance and deposits List fees not in checkbook Enter interest payment Total fees and interest Checkbook balance Errors & Cancelled checks Any error should be verified with bank & corrected as necessary Cancelled checks – The actual check written and deposited may be returned with statement Most banks keep these now (Truncated) CHECKING ACCOUNT FEES Monthly maintenance fee – flat fee no matter how many checks you write. Service Charge – a special charge for each check you write or other special services ATM Fees Electronic Banking Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) – move money from one account to another automatically Example: Checking into Savings Automatic Bills Payments – pay bills by phone after bank notification (possible banks fee) Direct Deposit – paychecks deposited directly into your checking account (you get stub) Debit Cards – cards are used like credit cards but money spent is automatically deducted from checking account Automatic Withdrawals – bank removes money from the account at a specified time and sends it to a company to pay bill (Example: mortgage or insurance payments) Automated Teller Machines (ATM) Automated Teller Machines (ATM) • • • • • make deposits withdraw cash transfer money between accounts check your balance pay some bills Personal Identification Number (PIN) – Secret number that identifies you to the ATM as the owner of the card Choose a bank with locations you will use to avoid service fees Online Banking Complete transactions online Register through your bank to do this There is often a monthly service fee Electronic Fund Transfer Act – (EFTA) requires banks to inform the customers of fees and supply receipts for electronic transactions. Guaranteed Payment Checks Certified Checks – Personal check stamped and signed by a bank officer - stamp guarantees that account has the funds to cover the check Cashier’s Check – Bank’s own personal check signed by bank cashier - $25 fee Money Order – Check that draws on the money of the bank or other financial company that issue it - Buy one from a bank , post office, currency exchange Traveler’s Check Check that you pay for in advance, and if they are stolen or lost, the company you bought them from replaces them Purchase at banks, travel agency, etc There is usually a small fee. Safe Deposit Boxes Boxes with individual locks that you may rent from a bank Located in the vault Cost of a small box is usually $30 – 40 a year Important papers - birth certificates Small valuable items - Jewelry Wire Transfers Electronic communication moving money from one account to another Usually $20-$40 fee through banks Other financial organizations may also provide this service Homework