Sequential Circuits-Radha Iyer[cs 151]
advertisement
![Sequential Circuits-Radha Iyer[cs 151]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009253826_1-9ea30ee9b3f2c51b0308a42ccf258b21-768x994.png)
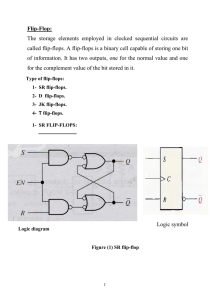
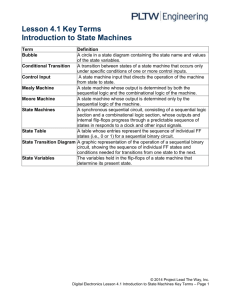
FLIP-FLOP AND FINITE STATE MACHINE By: Radha Iyer Prof: Dr. Sin-Min Lee CS147 Computer Organization and Architecture WHAT IS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS? A Sequential Circuit can be defined as circuit having sequential logic. Sequential logic is a type of a logic circuit whose output depends not only on current inputs but also on previous inputs. WHAT ARE FLIP-FLOPS? In order to remember previous inputs, sequential circuits must have some sort of storage element. This storage element is called “flip-flop”. Flip-flop depends on previous inputs to the circuit. The basic memory unit is called an SR flip-flop. We can describe flip-flops using characteristic table. SR Flip-Flop operation (BUILT WITH NOR GATES) Characteristic table [6] Excitation table S R Action Q(t) Q(t+1) S R Action 0 0 Keep state 0 0 0 X No change 0 1 Q=0 0 1 1 0 reset 1 0 Q=1 1 0 0 1 set 1 Unstabl e 1 combina tion 0 race conditio n 1 1 X UNSTABLE CIRCUIT S-stands for set R- stands for re-set If both S and R are set to1 in the SR flip-flop at the same time then it resulted in an unstable circuit, so this combination is not allowed. To take care of this problem JK flip-flops were developed. WHAT IS JK FLIP-FLOP? It is a variation to SR flip-flop, but it takes care of the S=R=1 combination. (J=Set, K=Reset) When it comes to the S=R=1 it toggles. It is a great improvement over the SR flip-flops. JK Flip Flop operation [6] Characteristic table Excitation table Comm Q ent Qnext J K Comm ent 0 hold state 0 0 0 X No change 0 1 reset 0 1 1 X Set 1 0 set 1 0 X 1 Reset 1 1 toggle 1 1 X 0 No change J K 0 Qnext WHAT ARE D FLIP-FLOPS? Another modified version of SR flip-flops are D flip-flops. ‘D’ stands for data flip-flops. It represents physical computer memory. The output always takes on the state of the D input at the rising clock edge. D flip-flops are very useful as they capture the signal when the clock rises. Flip-flops are very useful and are found in a lot of electronic devices. Truth table: Clock D Q Qprev Rising edge 0 0 X Rising edge 1 1 X Non-Rising X Qprev FINITE STATE MACHINE It is a model of behavior composed of a finite number of states, transitions between those states, and actions, (wikipedia,2000). A finite state machine is an abstract model of a machine with a primitive internal memory. It depicts the graphical part of the flip-flops. MOORE/MEALY MACHINE’S Moore machine represents the JK flip-flops Output depends only on the state. Example for the Moore machine model will be the elevator door, which just open’s and closes Mealy Machine depends on output and state. Example of Mealy Machine will be Microwave oven. MEALY MACHINE FOR JK FLIP-FLOPS CONCLUSION We learned about flip-flops which are basic storage elements. There were different kinds of flip-flops versions developed SR, JK, D flip-flops. Then we learned about Finite State Machines which are primitive internal memory. We saw Moore Machine, Mealy Machine which are types of Finite State machines. SOURCES http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flip-flop_(electronics) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Finite-state_machine