Topic 4: Competition and Market Structure
advertisement

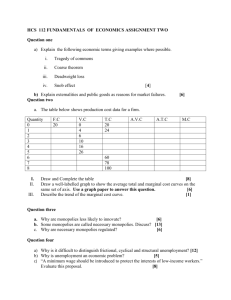
Topic 4: Competition and Market Structure I. Perfect Competition A. Conditions for Pure Competition *Def: Pure Competition 1. Many buyers and sellers participate in market 2. Sellers offer identical products 3. Buyers & sellers are well informed about products 4. Sellers are able to enter and exit the market easily. *What controls price in a market with pure competition? I. Perfect Competition B. Barriers to Entry & Competition * Barriers to entry can lead to imperfect competition 1. High Start-Up Costs 2. Complex Technology *Ex of business with high start up costs? Low start up costs? I. Perfect Competition C. Price, Output, and Purely Competitive Markets 1. Purely competitive markets are efficient. 2. Competition keeps both prices and production costs low. 3. Output in a purely competitive market will reach the point where suppliers just covers its costs and makes minimal profit *Who likes a purely competitive market more, consumers or producers? Why? II. Monopolies A. Characteristics of a Monopoly Definition: • • • • Single seller controls the entire market Barriers prevent firms from entering the mkt Supplies a unique product can’t get anywhere else; no close substitute Monopolies can take advantage of the market power and charge high prices II. Monopolies A. Characteristics 1. Economies of Scale *Def: factors that cause a producer’s average cost per unit to fall as output arises • Figure 4.2 • Bigger is better • Ex: hydroelectric plant II. Monopolies A. Characteristics * Natural Monopolies: a market that runs most efficiently when one large firm provides all the output. Ex: water companies • What is the one characteristic all types of monopolies have in common? II. Monopolies B. Price Discrimination 1. If monopolist sets price at the max price in the mkt, can limit who will be able to purchase good 2. Offers different prices: price discrimination 3. Target discounts * Discounted airline fares * Manufacturer’s rebate offers * Senior citizen/student discount s * Children stay free III. Monopolistic Competition & Oligopoly A. Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition * Def: products are similar but not identical Four Conditions 1. 2. 3. 4. Many firms Few artificial barriers to entry Little control over price Differentiated products III. Monopolistic Competition B. Non-price Competition * Competition through other ways besides lower prices 1. 2. 3. 4. Physical Characteristics Location Service Level Advertising III. Oligopoly A. Characteristics of Oligopoly *Def: mkt dominated by a few large, profitable firms. 1. Barriers to Entry 2. Cooperation & Collusion… price war, collusion, price fixing 3. Cartels: more formal than collusion • Why is a price war harmful to producers? IV. Government Regulation & Competition A. Market Power & Predatory Pricing 1. Monopolies & oligopolies have mkt power: the ability to control prices and mkt output. 2. Will want higher prices and lower output…reduced competition. 3. Engage in predatory pricing… drive competitors out of business IV. Government Regulation B. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Government & Competition Anti-Trust Laws: Sherman, Clayton Regulating Business Practices Splitting Up Monopolies Assessing Mergers Merger Guidelines *What kinds of rules and regulation does the government use to break up monopolies? IV. Government Regulation C. Deregulation 1. Definition: govt no longer decides what role each company can play in a mkt. 2. Recent deregulated industries: airline, trucking, banking, railroad, natural gas, tv. 3. Allowed/ forced firms in these industries to compete by eliminating price controls and barriers to entry 4. Airline regulation: mixed results ** Deregulation weakens govt controls; anti-trust laws strengthen it. Same purpose: promote competition