bread jmb
advertisement

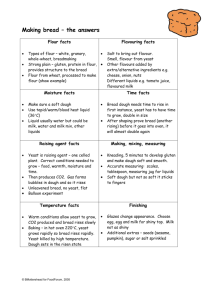
BREAD BASIC RECIPE 500G STRONG PLAIN FLOUR 10G SALT 1 SACHET EASY BLEND (DRIED) YEAST 250ML WATER (37C) FUNCTIONS OF INGREDIENTS FLOUR Flour is the main ingredient and forms the framework of the bread Strong plain flour is used as it contains a high percentage of protein. When mixed with water it forms gluten which helps to give the final product its shape Dextrinisation takes place when the bread is cooked. The starch in the flour is converted into dextrin (a simple sugar), which is caramelised and gives the crust its colour Water Water Water helps to develop the gluten in the flour Binds the ingredients together Water is needed for the yeast to ferment Salt Salt Adds flavour Aids the development of gluten Too much salt can kill off the yeast Fat and Oil Fat and oil These weaken the gluten and restrict the action of yeast. This gives a closer texture Fat helps to keep the bread fresh YEAST YEAST Yeast is a single celled organism found naturally on the skins of fruit and in the air. It is also grown commercially and sold as fresh, quick-acting or dried. Yeast needs FOOD WARMTH (37C), any higher it will be killed, lower and it works more slowly MOISTURE TIME FERMENTATION-HOW YEAST WORKS In the right conditions yeast will reproduce and increase in number. As they do alcohol, carbon dioxide gas are produced. The bubbles of gas are held in the stretchy framework of the dough and so the dough grows in size Once risen the dough must be put into a very hot oven to kill the yeast YEAST + SUGAR + WATER= CO2 + ALCOHOL FERMENTATION-TIMESCALE = 20 MINUTES 1 Yeast Cell Starts to bud Doubles in Size Almost splits Two separate cells KNEADING This is an important part of bread making It develops the gluten and makes the gluten stretchy and strong so that dough will hold its risen shape Rising the dough Best done in a warm place. Too cool a temperature and the rising process takes a long time Too hot a temperature will kill off yeast Cover the dough during rising to prevent a hard skin forming Baking Bake at a hot temperature to kill off the yeast and the bread will bake in its risen shape Test to see if cooked by turning out of tin and tapping on underneath. It should sound hollow Questions 1. Why is it essential to use strong flour in 2. 3. 4. 5. breadmaking? What is gluten What conditions are needed for yeast to grow Explain how the yeast causes the dough to rise Why is it necessary to knead bread CHORLEY WOOD METHOD This is a quick method of bread making often used commercially. Extra yeast and water are used and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is also added There is extensive kneading before shaping FAULTS IN BREAD MAKING LOAF SMALL AND DENSE Insufficient fermentation Insufficient liquid resulting in a dough which is too stiff to allow expansion Inactive yeast which has not produced sufficient CO2 LOAF NOT RISEN,HARD AND WITH A COURSE TEXTURE Dough is over fermented. Gas pockets break down and CO2 released leaving large uneven holes Yeast is killed before the loaf is baked