Yeast breads - Marblehead High School
advertisement

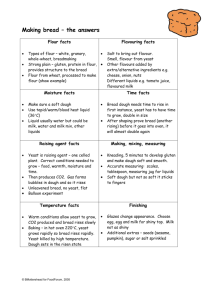
Yeast Breads Ingredients Yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae, cells metabolize sugar (fructose, glucose, sucrose, maltose) and release CO2. C6H12O6 --> 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2 glucose ethyl alcohol carbon dioxide Yeast also effects elasticity, stickiness, and flow properties. Flour - high protein content for good gluten development. Liquid - dissolution, hydration, and gelatinization. Salt - flavor, also favors amylase action and inhibits protein splitting enzymes. Sugar - fermentable sugar for yeast. Problems Excess flour - stiff inelastic dough, slow to rise, limited expansion in baking, cells small, thick walls, small volume. Excess sugar - above 10% sugar inhibits yeast, delays water uptake by flour. Yeast - 1/3 to 1 1/3 packages per 1 1/2 cups flour. Too little increases rising time. Too much causes inflation prior to other changes. Gives yeasty flavor. Basic Methods of Making Yeast Bread Straight dough - liquid warmed with sugar, salt and fat. Cooled, yeast is added to mixture. Flour added, beaten, more flour, kneaded, then raised. Batter or No Knead - more liquid, gluten develops in bowl as batter is beaten. Sponge - liquid, sugar, yeast, and part of the flour are mixed. Allowed to become light and fluffy in bowl, remainder of flour, fat, and salt are added. Kneaded and raised. Principles Kneading - allows development of strong elastic gluten. Fermentation - period where dough is allowed to rise in bowl and yeast produces leavening gas. Punching - light kneading after fermentation prior to shaping. Proofing - final rising in the pan after dough is shaped. Ovenspring - rapid increase in loaf volume when first put into the over for baking. Other Yeast Products Rolls-Kaiser, submarine, hot dog, hamburger, etc Pita bread Bagels English muffins Pizza crust Pretzels/Bread Sticks Raised doughnuts Choice of Breadstuffs Select whole grain or enriched, avoid sweet and rich items. Choice influenced by family preference, convenience and time savings and cost. Ready-to-serve Bake and eat Package mixes Bread Staling Crust becomes tough and leathery Crumb is dry, harsh and crumbly Theorized due to aggregation of amylose molecules, recrystallization of amylopectin molecules sometimes called retrogradation, or the transfer of moisture from gluten to the starch. Delay by: covering and storing at 60 C or 140 F or freezing