PPT - Electron Configuration
advertisement
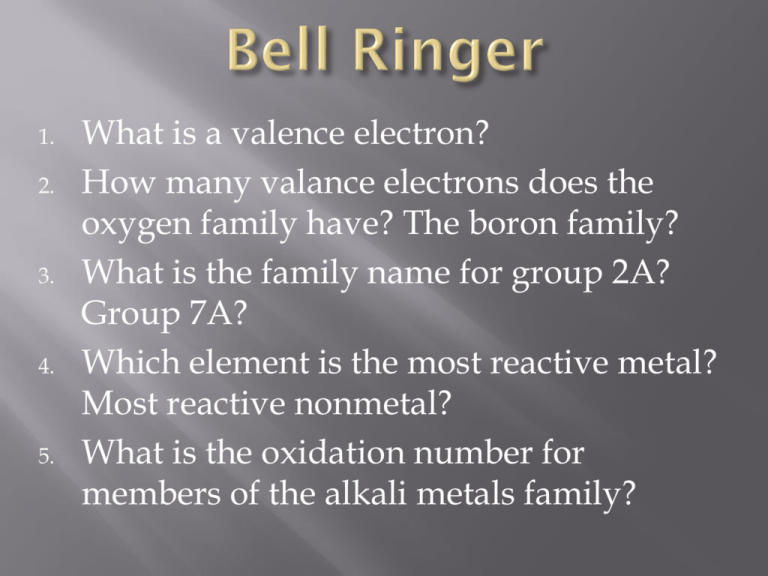
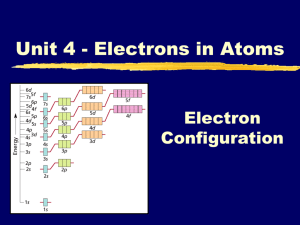
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is a valence electron? How many valance electrons does the oxygen family have? The boron family? What is the family name for group 2A? Group 7A? Which element is the most reactive metal? Most reactive nonmetal? What is the oxidation number for members of the alkali metals family? MODERN VIEWS OF THE ATOM • 4 Quantum Numbers: • Principal QN (n) refers to the energy level. • Secondary or angular QN (l) indicates the sublevel (s, p, d, or f) • Sublevels: • s = 2 e- max p = 6 e- d = 10 e- f = 14 e• Magnetic QN (ml) indicates the orbital the electron is in • px, py or pz • Spin QN (ms) indicates the direction the electron is spinning (left or right) • ½ or –½ “s” = “p” = SHAPE OF D Shape of f MIND BLOWING!! • Just imagine an atom with for example 92 electrons like Uranium. All are whizzing around the nucleus at the speed of light in different shaped paths. Video orbitals! http://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=KjNgq16jEY&feature=related THERE ARE RULES! • Aufbau Rule: Electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first. • Hund’s Rule: States that single electrons must occupy separate orbitals before pairing up. • Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two electrons in an atom have all 4 quantum numbers the same. One quantum number must be different. Aka SPIN! THE “ARROW” DIAGRAM Electrons arrange themselves in orbitals of increasing energy. Examples: N Al K s = 2 p = 6 d= 10 f = 14 Br Ag ELECTRON CONFIGURATION (LONG FORM) • This gives MORE information about predicting properties. • The placement of an elements electrons is written as: 4th Energy level 6 4p 6 electrons These add up to total # of e- Sublevel p 2 1s , 2 2s , How many total electrons? What element is it? 6 2p , 2 3s , 6 3p s Block 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s p Block d Block 3d 4d 5d 6d f Block 4f 5f 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 7p







![The electronic configuration of phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008974852_1-8381577ce936fbfa611892c1a5f109cd-300x300.png)