Psychosocial Stages of Development
advertisement

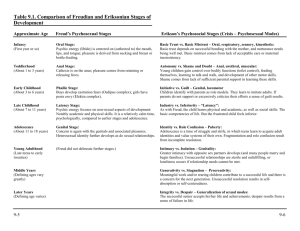
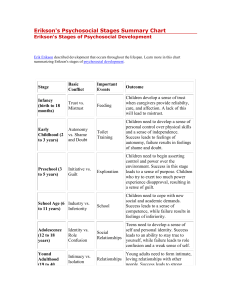
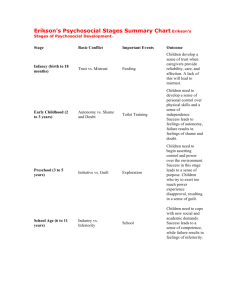
Psychosocial Stages of Development Erik Erikson Psychosocial • Psyco = psychological • Social = environment o Interaction of both o Reciprocal relationship • Erikson put together 8 stages of development o Stages = crisis to be resolved for that stage of development • If crisis is not resolved the other stages can be effective and the person’s growth can stagnate • Not everyone goes through the stages as quickly as others • Ages are attached to each stage but are not concrete 1. Trust vs. Mistrust • Child must learn trust by having needs met consistently or they will carry an inner sense of mistrust into future relationships • Basic Needs: food, diaper changes, interaction, bathing, clothes, mental stimulation, protection • You can’t spoil a baby for the 1st year of life 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt • Individuation: Child discovers that Mom and me are separate • They learn to start exercising their own will or they will feel shameful about becoming their own person. • If this stage is resolved they may become a dependent person later on in life • Shape their will but don’t break their will • Unmet needs in some Mothers can cause them to desire to feel needed/wanted and not allow this growth stage in their child • Ex. Let toddlers wash their own hands, put on their clothes, feed themselves, potty train, etc. 3. Initiative vs. Guilt • Child must learn to initiate tasks and conversations. • If a parent “takes over” child will feel guilty and stop initiating. • If this stage is not successful, this can lead to difficulty in making decisions later in life. • Ex. Allow them to clean up toys, make their bed, get dressed, put dishes in dishwasher, etc. If you go in and remake their bed you are telling them they are not good enough. 4. Competence vs. Inferiority • Child must feel like they are competent in something or they will feel inferior to others. • Ex. Start a sport, start playing an instrument. • Find out what the child is good at it and praise him! • Warning: comparing children breads anger and jealousy in children 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion • Adolescence develops a “sense of self” and purpose in life. If not, then they become confused as to their role in life. • Identity: who you are without anything else around you. • Parents should give their teens specific responsibilities and increase those responsibilities • Ex. Babysitting, get a volunteer job, consistent required chores, getting a job, taking leadership roles in a club/organization, etc. Types of Identity 1. Foreclosure: formed early by taking on family values, beliefs, and expectations of the parents without knowing why. 2. Negative Identity: Formed in opposition to what is expected. Ex. Conformity to peer groups—reacting against something like parenting style 3. Identity Diffusion: confused about what is expected and doesn’t seem to care to figure out his/her identity 4. Identity Achievement: Knowing who you are and why you believe what you believe. This is achieved through a time of asking questions 5. Moratorium: a time of exploring beliefs, interests, etc. Primary age is late adolescence through first few years of college 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation • The young adult learns to establish close relationships by being open and REAL with others OR is unable to develop close relationships and lives in isolation • Once you’ve established who you are (stage 5) you are safe to be in a relationship with someone else so you don’t base your identity off the other person Differences in Developing Intimacy Guys: Goal Oriented • Wrestle, play sports • Do activities together • Action oriented • Solution Focused Ladies: Journey Focused • Talk • Stop and do things a long the way • Interdependent • It’s all about the experience & details 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation • Middle age either feel like they are giving back to future generations OR a lack of purpose, feel unproductive, become self absorbed and stagnate. • This is a time to reevaluate life and ask, “Have I accomplished what I wanted in life?” 8. Integrity vs. Despair • Old age brings thoughts of the end of life. People in this stage either feel good about themselves that they have achieved their goals and that life has meaning or they are dissatisfied and feel like they have missed opportunities and fall into despair. • Reflect on one’s life time line and face life’s end Journal Reflect on your life and the different stages of development. Describe they stage you are currently in as well as success and failures from previous stages that might effect who you are today. Give examples that justify your success/failure for each stage.