ATP Storing and Releasing Free Energy
advertisement

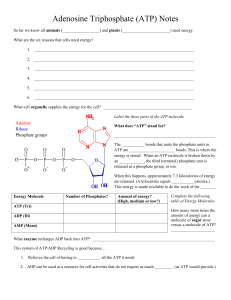
ATP Storing and Releasing Free Energy Chemical Energy Life processes require a constant supply of energy. Nutrients supply organisms with energy and raw materials The energy contained within the nutrient molecules is known as chemical energy. Chemical Energy Bond energy between the atoms of a nutrient molecule is known as chemical energy. Organisms ingest nutrients for chemical energy and raw materials. Cellular Respiration Chemical energy found in nutrients gets converted into free energy (energy that is available to do work) by a process known as cellular respiration. Free Energy Energy that is immediately available for cells is known as free energy. The ATP molecule is a molecule that stores and releases free energy. ATP The letters ATP stand for Adenosine Triphosphate. Adenosine = Adenine (a nitrogen base) and Ribose (a five carbon sugar) Triphosphate = Three phosphates bonded together in a straight line. Structure of ATP Molecule Structure of ATP Molecule Examine the ATP Molecule Look for the nitrogen base called adenine. It is a double-ringed structure Look for the 5 carbon sugar called ribose Examine the three phosphates bonded in a straight line. Releasing Free Energy The Bonds between the phosphates contain free energy. Chop off the terminal phosphate and free energy is released. A-P-P~P. The terminal phosphate contains the most energy. Equation for Releasing Free Energy A-P-P~P A-P-P + free energy + P Notice that ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) becomes ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) Storing Free Energy When the cell has free energy that needs to be temporarily stored, ATP is formed from ADP. ADP stands for Adenosine DiPhosphate Putting a phosphate back onto ATP stores free energy. Equation for Storing Free Energy A-P-P + P + Free energy A-P-P~P Chemical Reactions: Condensation and Hydrolysis Storing Free Energy means putting a phosphate onto ADP Condensation is required to put the phosphate onto ADP. Releasing Free Energy means chopping off the terminal phosphate from ATP Hydrolysis is required to chop off a phosphate from ATP Hydrolysis of ATP Hydrolysis of ATP is used by the cell to provide the energy needed to drive the chemical reactions that enable an organism to function. Dehydration Synthesis aka Condensation A Condensation (aka Dehydration Synthesis) reaction is required to store free energy onto an ADP molecule forming ATP. ATP A large macromolecule that stores and releases free energy. Keep Studying Biochemistry