ATP student notes
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Notes
So far we know all animals (__________________) and plants (_______________________) need energy.
What are the six reasons that cells need energy?
1.
_____________________________________________________________________________
2.
_____________________________________________________________________________
3.
_____________________________________________________________________________
4.
_____________________________________________________________________________
5.
_____________________________________________________________________________
6.
_____________________________________________________________________________
What cell organelle supplies the energy for the cell? ___________________________________________
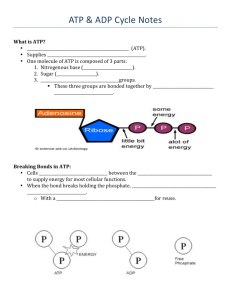
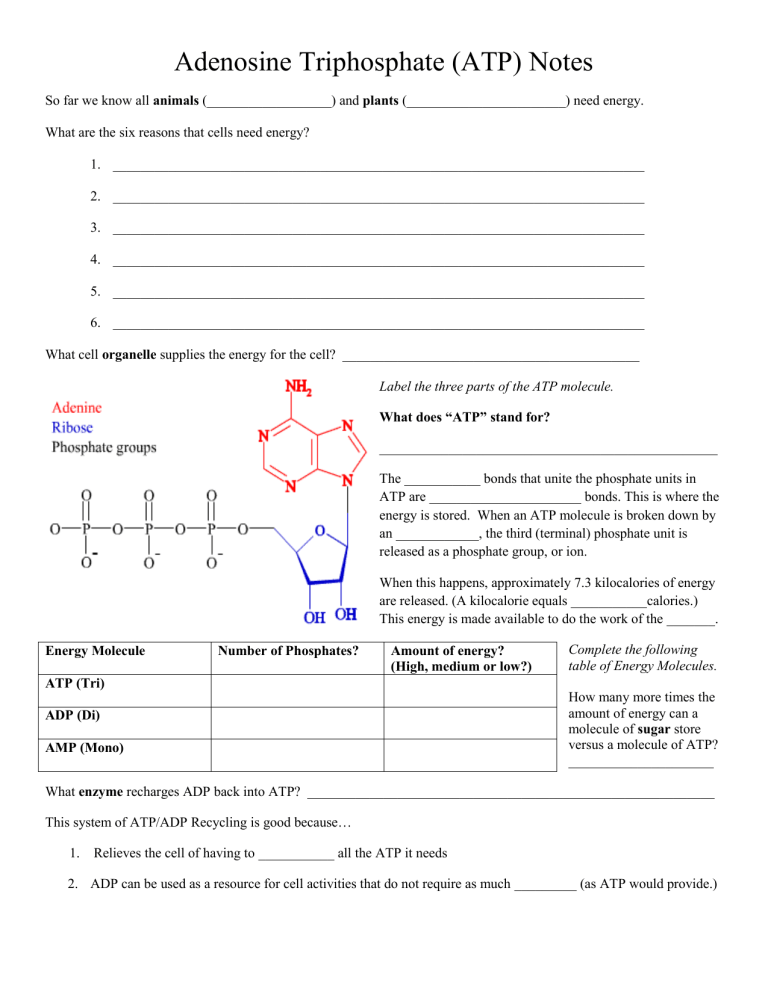
Label the three parts of the ATP molecule.
What does “ATP” stand for?
_________________________________________________
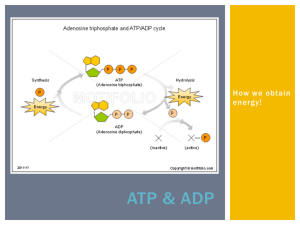
The ___________ bonds that unite the phosphate units in
ATP are ______________________ bonds. This is where the energy is stored. When an ATP molecule is broken down by an ____________, the third (terminal) phosphate unit is released as a phosphate group, or ion.
When this happens, approximately 7.3 kilocalories of energy are released. (A kilocalorie equals ___________calories.)
This energy is made available to do the work of the _______.
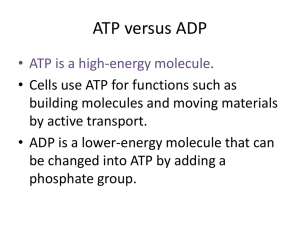
Energy Molecule
ATP (Tri)
ADP (Di)
AMP (Mono)
Number of Phosphates? Amount of energy?
(High, medium or low?)
Complete the following table of Energy Molecules.
How many more times the amount of energy can a molecule of sugar store versus a molecule of ATP?
_____________________
What enzyme recharges ADP back into ATP? ___________________________________________________________
This system of ATP/ADP Recycling is good because…
1. Relieves the cell of having to ___________ all the ATP it needs
2.
ADP can be used as a resource for cell activities that do not require as much _________ (as ATP would provide.)