Adolescence - AP Psychology Community
advertisement

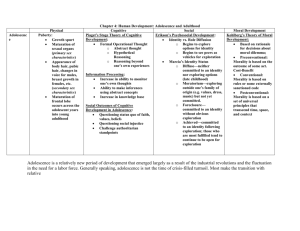
Adolescence (Halloween Special) The transition period from childhood to adulthood. Is adolescence getting longer or shorter? Physical Development • It all begins with puberty Puberty: the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing. Primary Sexual Characteristics • The body structures that make sexual reproduction possible Ovaries Vagina Testicles Penis Secondary Sexual Characteristics • Nonreproductive sexual characteristics Female breasts Deepening of male voice Body hair Jalo’s Hips When does puberty start? The Landmarks • First ejaculation for boys •Menarche for girls Do we remember these things? Puberty Sequence is way more predictable than the timing. How might timing differences effect an adolescent socially? Cognitive Development • Have the ability to reason but……. •The reasoning is self-focused. Assume that their experiences are unique. •Experience formal operational thought Lawrence Kohlberg and his stages of Morality • Preconventional Morality • Conventional Morality • Postconventional Morality Preconventional Morality • Morality of self- interest • Their actions are either to avoid punishment or to gain rewards. Conventional Morality Morality is based upon obeying laws to 1. Maintain social order 2. To gain social approval Postconventional Morality • Morality based on your own ethical principles. Talk is Cheap How do we turn morality into action? • Teach Empathy • Self-discipline to delay gratification • Modal moral behavior Social Development Its all about forming an identity!!! Identity • One’s sense of self. • The idea that an adolescent’s job is to find oneself by testing various roles. • Comes from Erik Erikson’s stages of Psychosocial development. Identity • Some teenagers take their identity early by sharing their parents values and expectations. • Some teenagers will adopt a negative identity- opposition to society, but conforms to a peer group. Intimacy • Towards the end of adolescence, intimacy becomes the prime goal. • Can you list the intimacy differences between men and women? Trust vs. Mistrust Age Birth - 18 months Important Description Event Feeding Infants form a loving, trusting relationship with parents; they also learn to mistrust others. Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Age 18 months - 3 Years Important Event Toilet Training Description Child's energies are directed toward physical skills: walking, grasping, and toilet training. The child learns control along with a healthy dose of shame and doubt. Initiative vs. Guilt Age Important Description Event 3 - 6 Years Independence Child becomes more assertive, takes more initiative, becomes more forceful. Competence vs. Inferiority Age 6 - 12 Years Important Description Event School The child must deal with demands to learn new skills while risking a sense of inferiority and failure Identity vs. Role Confusion Age Important Description Event Adolescence Peers Teens must achieve self-identity while deciphering their roles in occupation, politics, and religion. Intimacy vs. Isolation Age Important Description Event Young Adult Relationships The young adult must develop marriage-seeking relationships while combating feelings of isolation. Generativity vs. Stagnation Age Important Description Event Middle Adult Parenting Assuming the role of parents signifies the need to continue the generations while avoiding the inevitable feeling of failure. Integrity vs. Despair Age Late Adult Important Description Event Life Acceptance of Reflection one's lifetime accomplishments and sense of fulfillment.