School presentation design template
advertisement

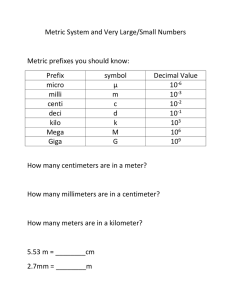
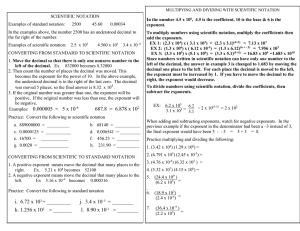
Measurement I. Measurement A. A quantity that has both a number and a unit 1. Which is a measurement? i. 12 cm ii. 134.54 iii. 0.0034 II. The Metric System A. Standard units of measurement (SI) Quantity Length Unit meter Symbol m Mass Temperature Time Amount of substance kilogram Kelvin second mole kg K s mol B. Temperature conversion: °C + 273 = Kelvin III. Metric Prefixes Prefix Kilo (k) Centi (c) Milli (m) Micro (μ) Nano (n) Meaning 1000 times larger than the unit 100 times smaller than the unit 1000 times smaller than the unit 1 million times smaller than the unit 1 billion times smaller than the unit Factor 103 10−2 10−3 10−6 10−9 IV. Scientific Notation A. Used to write really big and small numbers 6.02 ×1023 B. The coefficient is equal to or greater than 1 and less than 10 C. The exponent is a positive or negative integer V. Writing Scientific Notation A. For large numbers— 1. move the decimal to the left until one digit remains in front 2. Count the number of times the decimal moves 3. The exponent is positive 4. Example: i. 3,000 3 103 ii. 405,000 4.05 105 B. For small numbers— 1. move the decimal to the right until one digit is in front 2. Count the number of times the decimal moves 3. The exponent is negative 4. Example: i. 0.00034 3.4 10−4 ii. 0.0000005070 4.05 10−6 VI. Accuracy A. How close a measurement comes to the actual value of whatever is measured B. The more # of significant digits, the more accurate the value VII. Precision A. How close a series of measurements are to one another or “repeatability” B. You must compare two or more measurements to each other VIII. Accuracy vs Precision A. Example: Jack has a height of 70 inches. Which sets of measurements are 1. Accurate and precise 2. Precise but not accurate 3. Neither precise nor accurate i. 69.5 in., 70.5 in., 70.1 in. ii. 45.3 in., 62.1 in., 84.3 in iii. 78.3 in., 78.0 in., 78.1 in IX. Percent Error A. To find out how close you are to an accepted or actual value error B. Percent error = exp val – act val act val x 100% C. Example: Your data reads 99.1g but the accepted value is 101.0g, what is your percent error? Percent error = 99.1g − 101.0g 101.0g %error = 1.88% × 100