Theories of Personality
advertisement

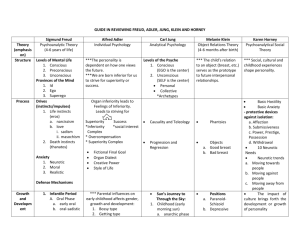
Theories of Personality Sigmund FreudPsychoanalytic Theory • One of the founding fathers of the Psychoanalytic school of Psychology • Also, the father of psychoanalysis • The mentor of famous Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung **Psychoanalytic Theory stresses the importance of the unconscious mind on our behavior Three processes at work The ID- a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that strives to satisfy basic sexual & aggressive drives. The ID operates on the “pleasure principle”, demanding immediate gratification The Superego- the part of the personality represents internalized ideals & provides standards for judgment (the conscience). Shaped by our parents and societal expectations Three processes at work The Ego- the largely conscious “executive part of personality that mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and personality. The ego operates on the “reality principle”. Other Freudian ideas at work…. Oedipus Complex leads to…. Identification- the process by which, according to Freud, children incorporate their parents’ values into their developing superegos. Psychosexual Stages (check out on the wiki!) Fixation- a lingering focus of pleasure seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage in which conflicts were unresolved Defense Mechanisms How do we deal if things don’t go the way we’d like, if we have unresolved issues within the unconscious? Freud says we use: Defense Mechanisms- in psychoanalytic theory, the ego’s productive methods reducing anxiety arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness Defense Mechanisms Repression- The process of pulling thoughts into the unconscious and preventing painful or dangerous thoughts from entering consciousness Rationalization- The process of constructing a logical justification for a decision that was originally arrived at through a difference mental process among others….. Projective Tests, etc. Projective tests- a personality test, such as a Rorschach, that provides ambiguous stimuli designed to trigger projection of one’s unconscious thoughts and feelings Terror Management Theory- a theory of death-related anxiety; explores people’s emotional and behavioral responses to reminders of their impending death Neo-Freudian/Psychodynamic Theories of Personality *Psychiatrists such as Alfred Adler, Karen Horney, and Carl Jung began to emphasize childhood social interactions and their impact on the unconscious rather than tension produced by sexual and violent urges. *The unconscious still greatly impacts our behavior but we may manage this behavior more consciously. Alfred Adler -Austrian psychologist, 1870-1937 -broke away (or was broken away) from Freud and psychoanalytic psychology Inferiority Complex- Adler theorized, that due to our childhood interactions, some people may develop a lack of self worth, doubt, or see themselves as not living up to society’s standards. *This exists in the subconscious and may result in great achievement or asocial behavior. Karen Horney -German psychologist, 1885-1952 -founder of Feminist Psychology -argued against Freud’s theories regarding sexuality. She claimed that psychological differences in the sexes were rooted in societal and cultural influences and not biology. -”No” on Penis Envy! Carl Jung -Swiss psychologist, 1875-1961 -Freud’s #1 protégé’ -among many contributions to Psychology, Jung also played down the influence of sexual forces on the unconscious, breaking with Freud. Collective Unconscious- A part of the unconscious which all people inherit from our ancestors. Archetypes and other various themes and symbols are stored here as part of our human experience. Trait Theory Trait- a characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act, as assessed by self reported inventories and peer reports. Personality Inventory- a questionnaire on which people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings & behaviors used to assess selected personality traits Gordon Allport When interviewing Freud as a 22 year old student, Allport said that meeting with Freud, “taught me that psychoanalysis , for all its merits, may plunge too deep, and that psychologists would do well to give full recognition to manifest motives before probing the unconscious”. Allport’s work led to further studies of trait theory. Personality Inventories Myers-Briggs Trait Inventory Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory MMPI-2 Big 5 Factors Conscientiousness Agreeableness Neuroticism (emotional stability) Openness Extraversion (read pages 530-532) Humanist Theory -All people strive for perfection (of themselves) -People are like a seed who need to be nurtured -We are driven to satisfy needs -Much more positive view of people, focus on what makes us well rather than what makes us ill Humanist Theory-Maslow Remember Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs? Carl Rogers-Humanism Organism- the whole person-including all thoughts feelings that is seeking perfection Self (self-concept)- a person’s image of himself which is formed by the means of the responses of others Positive regard- the positive image people have of themselves because of unconditional approval by significant others in their lives Carl Rogers-Humanism Conditions of worth- the sense that people have of being worthy only if they behave in certain restrictive ways. Fully functioning person- a person whose self and organism are one and the same, allowing the openness to all feelings and experiences that develops personal completion and perfection Social-Cognitive Theory Social-Cognitive Perspective- views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people’s traits (including their thinking) and their social context. Albert Bandura Reciprocal Determinism The interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment The Need for Control Personal Control- the extent to which we perceive control over our environment External Locus of Control- the perception that chance or outside forces beyond our control determine our fate. Internal Locus of Control- the perception that you control your own fate Do We Control Our Own Fate? Self control- the ability to control impulses & delay short-term gratification for greater longterm results (Marshmallow test) Learned Helplessness- the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events A bit more about “the self”… Spotlight effect- overestimating others’ noticing and evaluating our appearance, performance, and blunders Self serving bias- a readiness to perceive oneself favorably Narcissism- excessive self love & self absorption