Chapter 3 Models of the Earth

1
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth
Section 1: Finding Locations on Earth
The Earth is divided into hemispheres, _____________ and ___________.
These hemispheres are then further divided into other areas.
Latitude
_____________________________________
Uses parallels as lines East and West of the equator
A parallel ____________________________________________
_______________________________________________
They are the same distance throughout the Earth’s Surface
Lat. of the equator is O o
North Pole is 90 o N. South Pole is 90 o S.
1 o of Lat is 1/360 of circumference 40,000
1 o of Lat is approx ________km
360
1 o = 60 minutes (60’) = _______km
1 second of lat = 1.85km
Longitude
Distance in degrees East or West of the Prime Meridian
Measured in meridians
A meridian _________________________________________
Furthest you can go is 180 o away (circle is 360 o )
Divided into degrees and minutes (1 o = 60’)
2
Closer the lines get together the further from the equator you are
At the equator 1 o is about as long as 1 o of latitude (111km), but the distance gets smaller the closer you are to the poles. The equator is a meridian.
Riverhead Long Island, New York is approx: 40 o 55’ 1”N 72 o 39’ 43”W
Greenport Long Island, New York is approx: 41 o 6” 12”N 72 o 21’3”W
Disney World, Florida is approx: 28 o 24’ 41” N 81 o 31’ 58” W
Great Circles
_________________________________________________________________
The equator is the only line of latitude that is a great circle. Meridians of longitude that cross over the north and south poles are also great circles. For every location on a great circle, it's antipodal location is also on the circle. Other than the equator itself, any great circle crosses the equator at two antipodal locations,
180° apart. Other than the equator and meridians of longitude that run due north and south, any great circle reaches its maximum latitudes at two locations that are 90° of longitude east and west of the two locations where the great circle crosses the equator.
Antipode – the location 180° on the other side of the world. Example 40 north’s antipode would be 40 south, and so on.
Prime Meridian - the longitudinal line that passes through Greenwich,
England O o Long (also passes through Spain, Algeria, Ghana, Burkina and Mali) It dates back to October 1884. At the behest of the President of the United
States of America 41 delegates from 25 nations met in Washington, DC, USA for the
International Meridian Conference
3
Finding Direction
Magnetic declination
_______________________________________________________
This number will change as you move around the earth. This is because a compass will point toward the magnetic north (also called the geomagnetic north) and we use polar north for direction without a compass
Global Positioning System
GPS
Tells position (latitude and longitude), speed and time (based on the global network)
If used by the military can be accurate to the centimeter
Found in most cars and can also be hand held with an accuracy of 10 to 15 meters.
Very accurate because it 3 satellites for triangulation for accuracy
Earth Observing System
EOS
Established in 1999
Unlike maps that show images, this system maps the changes in air from the ground to the atmosphere in all areas, even the water, it shows the exchange of carbon, water and energy. http://www-airs.jpl.nasa.gov/Technology/HistoricalContext/
4
Section 2 Mapping Earth's Surface
Cartography______________________________________________
Cartographer- ______________________________________________
Uses data collected from various sources.
Map - ________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
One Type of such a map is:
Remote Sensing – using satellites or airplanes to gather information without being there
Map projection
A map is flat so it is hard to show depth, they accomplish this by using a technique called map projection.
5
Map Projection: ______________________________________________
___________________________________________________
The three most popular map projections used today:
1.
______________________________________
It shows the whole world except extreme Polar Regions; shows true direction; polar region is exaggerated! Uses straight lines; looks like a grid. Used for sea navigation.
2. ___________________________________________
It shows that a straight line between two points is the shortest distance; direction and distance are not perfect. Looks like wedges - from the poles down. Used for air travel. Distorts both direction and distance
6
2.
________________________________________
Are a cone of a small area covered by these maps make them nearly correct in all aspects. Used by the U.S.G.S. (United States
Geologic Survey). Lines of lat. and long have slight curves.
When more than one conic map is used it is called Polyconic.
Reading Maps
Direction on a Map
You first need to figure out what ________________you are looking at.
Most maps drawn by the _____________________________ (USGS) has
North on top of the page. However, if north is not up on top they need a way of showing you direction by using a compass rose.
______________________ - usually a picture showing where North, East,
South, West are located. Some maps may use only a single arrow to do this. Some use an elaborate pointed symbol.
7
Symbols
A _________________ is a list of symbols and their meanings. They include urban, city or other areas.
Symbols are standardized colors:
Scales
Maps most also include a way to measure distances. They accomplish by using a scale.
1.
___________________ - is printed and looks like a ruler
2. _________________________
1/100 - map size is one-hundredth real size 1: 100
3. ____________________________
1 Centimeter represents 50 kilometers
______________________
Is a line of equal value. All points on the line are the same value.
This can be used for many different types of maps used in different sciences.
8
Section 3 Types of Maps
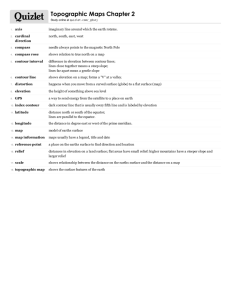
Topographic Maps
Part of the same map in a perspective shaded relief view illustrates how the contour lines of the original follow the terrain
Advantages of Topographic Maps
1.
Uses natural features and constructed features to represent an
area.
2.
They are made by using both aerial photos and survey points.
They show elevation.
3.
They are very detailed maps about the surface of an area, it will
cover all areas, size, shape, elevation.
4.
Uses isolines to show outlines of land forms.
________________ - exact elevation on a brass or Al Plate
- Done by U.S.G.S. to the nearest foot
- Labeled BM on maps
9
Elevation of Topographic Maps
Relief ___________________________________
1. Elevation - mountains, hills – High Points
2. Depressions - kettle holes, valleys – Low Points
Contour lines :
1.
___________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
2.
____________________________________________________
3.
__________________________________________________
Contour interval
___________________________________________________
Depression contours
1. Gives depression measurements
2. Drawn with lines on inside of contour intervals
10
Landforms on Topographic Maps
Any point on a contour line is exactly the elevation of the contour line
Any point between contour lines is an estimate in between the two contour lines
No contour lines - (few) very little change in elevation
A lot of contour lines - very steep change in elevation
Closed circles show tops of hills
A ridge is an oval contour line
Rivers - Contour lines always point upstream from where the river is flowing
Topographic Map Symbols a. Contour lines are brown b. Roads, buildings, railroads & works built by man are black c. Water is blue d. Woodland areas is green e. Highways are red f. Developed areas are pink
Profile-
To make a side view of the area on a topographic map. Also a cross sectional view of the area.
This important to see what the features would look like
11
Gradient = Change in elevation (Ft)
(Slope) distance (miles)
12
OTHER TYPES OF MAPS
_________________ - Shows distribution of geologic features
__________________ - show information about the soils in an area. Used by Natural Recourse Conservation Services (NRCS)