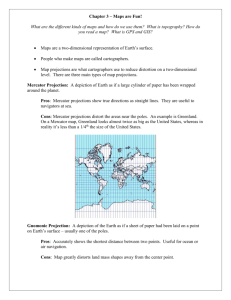
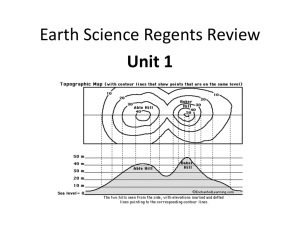
Point D is 60, what is the contour interval on the topographic map
advertisement

Point D is 60, what is the contour interval on the topographic map above?________________________ Identify the direction the river is flowing.___________________________________________________ Create a profile of line BC on the grid below. Calculate the gradient of line BC. Show all work including the formula. Identify the direction Mill River is flowing. ______________________________________________________ Create a profile of line XY on the grid below. Calculate the gradient of line XY. Show all work including the formula. (Estimate the field values based on proximity to index contours Earth’s Interior Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. As depth within the Earth increases, the density, pressure, and temperature increase. a. Example at a depth of 4,000km, the pressure will be approximately 2.3 millions of atmospheres and the temperature will be approximately 5,800oC When the inferred temperature is below the melting point=solid When the inferred temperature is above the melting point= liquid The outer core is the ONLY inferred layer that is liquid. Earth’s core (inner and outer) is inferred to be composed of iron and nickel. Pg. 1 ESRT “Average Chemical Composition” the two most abundant elements percent by volume= Oxygen and Silicon. Oxygen is the most abundant. Topographic Map Review Contour lines are isolines that are drawn on an elevation map. These lines connect all points with the same elevation, and give a great picture of the lay of the land. The resulting map is called a Topographic Map. There are several important rules to remember when reading a topographic map: Close line =Steep Slope Contour lines bend upstream when crossing a river- river flows downstream Highest possible elevation of a hill is the most inner contour line. Depressions are shown by small marks pointing inward off the contour line Calculating Gradient- Pg. 1 ESRT formula Change in field value= the change in elevation between two points- subtract Distance- use the scale to measure the distance between points. Size and Shape Review 1. From the Earth’s rotation, the shape of Earth is slightly off from a perfect circle and is called an oblate spheroid. 2. The best evidence is satellite imagery. 3. Latitude lines are horizontal and measure north and south from the equator. 4. Latitude lines are parallel. Latitude lines are also called parallels. 5. Longitude lines are vertical and measure east and west from the prime meridian. 6. Prime Meridian runs through Greenwich, England, Europe, Africa, and Antarctica. 7. Longitude lines converge at the poles and diverge at the equator. Plot the following points and label with coordinates- lat, long