Experiment 21
advertisement
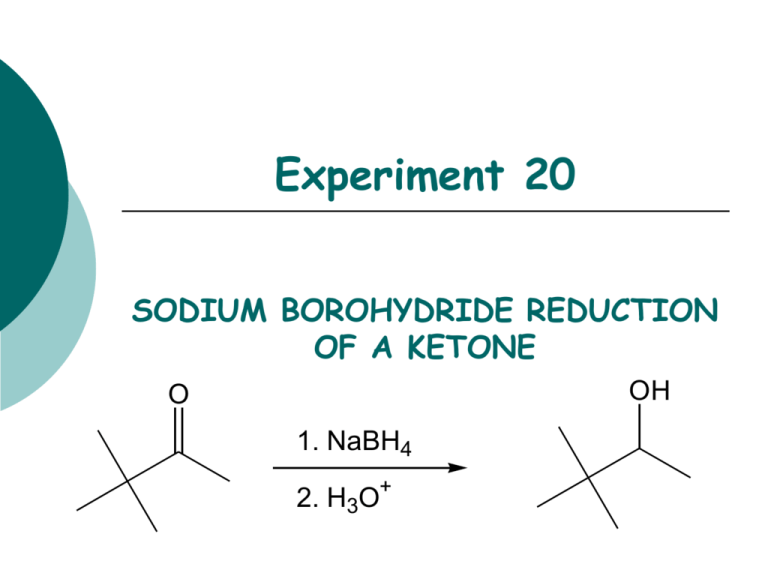
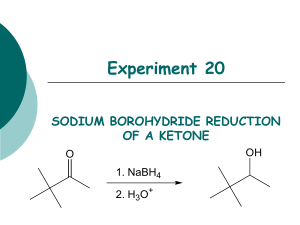
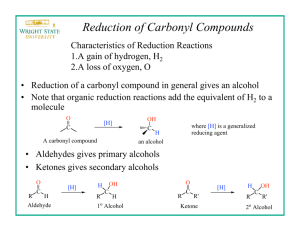
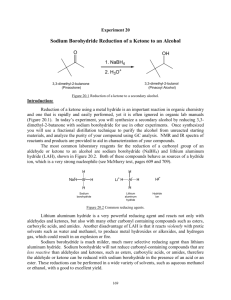
Experiment 20 SODIUM BOROHYDRIDE REDUCTION OF A KETONE OH O 1. NaBH4 2. H3O+ Objectives: To synthesize a tertiary alcohol from a ketone using a sodium borohydride reduction. To purify the product using fractional distillation. To analyze the purity of the product using GC. To characterize the reactants and products using NMR and IR spectroscopy. Before coming to lab… Review these techniques: Fractional distillation Vacuum filtration GC Analysis REDUCTION USING NaBH4 NaBH4 (sodium borohydride) is a versatile and useful reducing agent in organic chemistry. A reducing agent causes a reaction (a reduction) in which the product has more bonds from carbon to hydrogen (or fewer bond to oxygen) OH O 4 R C 4 R C R' + 1 NaBH4 then H2O H R' MECHANISM CH3O H3C C C CH3 CH3 H (from NaBH4) NaBH4 transfers a hydride ion to the carbonyl carbon. NaBH4 H CH3O H3C C C CH3H CH3 CH3OH O H H (from 6M HCl) The oxygen anion eventually removes a proton from water. H 3C C C CH3H CH3 TODAY’S REACTION O OH 4 (CH3)3CCCH3 + NaBH4 4 (CH3)3CCCH3 then H2O H Pinacolone Pinacolone is reduced using sodium borohydride. Note that ketone. 1 mole of NaBH4 will reduce 4 moles of EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis) Add 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone and methanol to 100 mL beaker. Place in ice water bath. Add NaBH4 while stirring with glass rod. Continue to react at 0oC for 5min, then 10 min more at RT. Add 6M HCl dropwise. Suction filter to remove separate solid from liquid filtrate. Transfer to 50 mL round bottom flask. 100 mL 50 mL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Purification and GC Analysis) Set up fractional distillation apparatus. Apply heat and collect distillate below 70oC in a small flask. Switch to 25 mL round bottom flask and collect distillate between 70-85oC. Cool flask, reweigh. Prepare GC sample. to voltage regulator water out water in heating mantle iron ring Table 20.1 Theoretical yield (g) Calculated based on limiting reactant Actual yield (g) Percent yield Distillation Range (oC) Product Appearance (Actual yield/Theoretical yield) X 100 Give Ti-Tf of distillate collected in 25 mL round bottom flask Give physical state and color of product Table 20.2 Atom Economy (%) Calculate based 3,3-dimethyl-2butanone and sodium borohydride ONLY! Experimental Atom Economy (%) “Eproduct” Cost per synthesis ($) Cost per gram ($/g) o Review Experiment 13 for calculations! WASTE MANAGEMENT o Place the solid boric acid waste from the filtration into the container labeled “SOLID WASTE” located in the waste hood. o Place all liquid waste into the container labeled “LIQUID WASTE”. SAFETY CONCERNS 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone, 3,3dimethyl-2-butanol, methanol and sodium borohydride are all FLAMMABLE materials. Methanol and sodium borohydride are TOXIC in large concentrations. Hydrochloric acid is CORROSIVE.