Lab Skills
advertisement
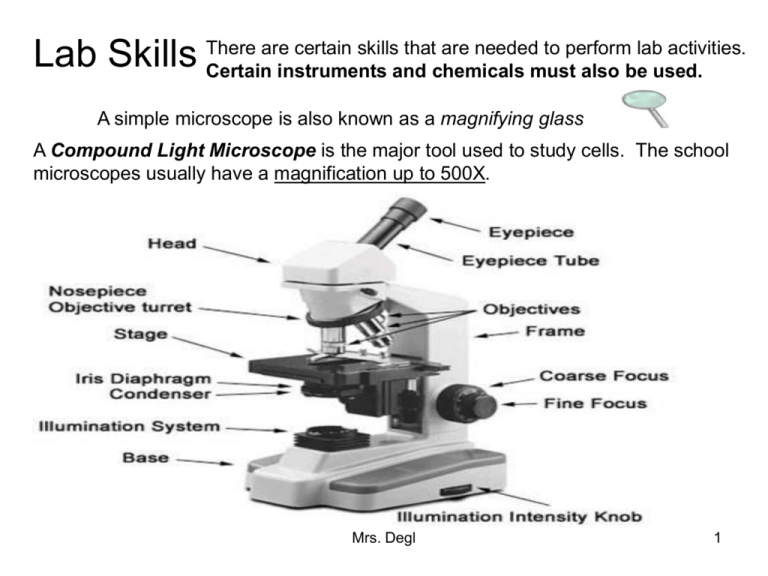
are certain skills that are needed to perform lab activities. Lab Skills There Certain instruments and chemicals must also be used. A simple microscope is also known as a magnifying glass A Compound Light Microscope is the major tool used to study cells. The school microscopes usually have a magnification up to 500X. Mrs. Degl 1 In a compound light microscope: The course adjustment is used to focus under low power. The fine adjustment is used to focus under high power and used to “fine tune” the image (make the image clearer). Total Magnification = Ocular (Eyepiece) X Objective Mrs. Degl 2 Some Key Points to remember when focusing on a specimen with the compound light microscope. 1.) The image of the specimen is reversed (backward) and inverted (upside down). 2. Do not touch the lenses. If they are dirty, ask the teacher for special lens paper or ask the teacher to clean the lenses for you. This is a letter F observed under low power with the compound microscope. Note that the image is reversed and inverted as seen by the viewer. Mrs. Degl 3 2.) Always begin focusing on the lowest possible power. Remember to center the specimen you are observing in the field of view before switching to a higher power. Make certain that you move the objectives away from the specimen when focusing so their is no collision between the objective being used and the slide/cover slip/specimen which may damage the objective lens. 3.) As you switch from low to high power, the field of view becomes darker. To deal with this the diaphragm needs to be opened to allow in more light. (Frequently on low power the diaphragm needs to be partially closed as it is too bright.) 4.) As you switch from low to high power the field of view becomes smaller. This decrease in size of the field of view is the inverse of the increase in magnification. For example if the magnification goes from 100 X to 400 X this is a four times increase in magnification, so the size of the field of view is quartered (X 1/4). Mrs. Degl 4 Estimating the Size of Specimens The size of a microscopic field of view can be determined on low power using a device called an optical micrometer. An economy version of this can be made by placing a clear metric ruler on the stage of a microscope and using it to estimate the field of view. An example of this appears below. If you observe the field of view at the left, it can be observed that there are approximately 3 1/2 divisions equal to a length of 3.5 mm. Therefore this field of view is equal to 3.5 mm or 3,500 micrometers. Remember that there are 1,000 micrometers in 1 mm (millimeter). Mrs. Degl 5 Solution: It can be noted that the two cells in this field take up a field of view of one millimeter. What is the average size of each cell in this field of view in micrometers? Therefore, the size of the specimen is equal to 1 mm/2 cells or 0.5 mm per cell. There is 500 micrometers in 0.5 mm., so the average size of each cell is 500 micrometers. Mrs. Degl 6 Solutions: 1.) It is sometimes tough to approximate the approximate size of the field of view, but this ameba Problem 1: The field of view under considered lengthwise appears to occupy approximately 1/3 of the low power on the left is equal to 3 field of view. mm. How large is this ameba in 3 mm X 1/3 = 1 mm length = 1,000 length in micrometers micrometers for the approximate (approximately)? length of this ameba. Problem 2: The second image on 2.) The student is viewing the the right is of the same organism same ameba on high power. The as the first image on the left in field of view gets smaller which problem # 1. What happened to makes the ameba appear larger in form the image on the right? this field. Mrs. Degl 7 Solution: Problem # 3: 3.) The increase in A student determines the magnification going from low field of view at 40 X power at 40 X to high power magnification using a at 100 X is 10 times. The compound microscope to be field of view will change 5 mm. The student then inversely to the increase in switches to high power with a magnification. Therefore, 5 total magnification of 400 X. mm. X 1/10 = 1/2 or 0.5 mm. which equals 500 What is the new calculated micrometers. Therefore the size of the field of view on field of view on high power in high power in micrometers? this example is 500 micrometers. Mrs. Degl 8 Electron Microscope Electron Microscopes are scientific instruments that use a beam of highly energetic electrons to examine objects on a very fine scale. It can magnify original image up to 250,000 times the original size. Allows for detailed observation of small organelles within the cell, like mitochondria. Capillary Image from EM Red Blood Cell Image from an EM Mrs. Degl 9 Dissecting Microscope Allows viewer to see the image in a three-dimensional view. Light cannot pass through the specimen (it is opaque), allowing for the three-dimensional view. These are used for dissecting small animals and plants. Mrs. Degl 10 Microscope Handling Rules 1. Always carry the microscope with two hands - one on the arm and one underneath the base of the microscope. Hold it up so that it does not hit tables or chairs. Never swing the microscope. 2. Do not touch the lenses. If they are dirty, ask the teacher for special lens paper or ask the teacher to clean the lenses for you. Teachers - you may use a soft cloth dipped in a small amount of isopropyl alcohol to clean the lenses. 3. If using a microscope with a mirror, do not use direct sunlight as the light source. Eye damage can result. If using a microscope with a light, turn off light when not in use. 4. Be cautious when handling glass slides and cover slips. Notify teacher if a slide or cover slip breaks. Students should not handle broken glass. 5. Always clean slides and microscope when finished. Store microscope set on the lowest objective with the nosepiece turned down to its lowest position (using the coarse adjustment knob). Turn off light. 6. Cover microscope with dust cover and return microscope to storage, if requested by teacher. Mrs. Degl 11 Centrifuges are used to separate cell parts based on density. Cells are spun around at high speeds. Micro-dissection Instruments Tools used to perform dissections of individual cells or smaller cell parts. They are most commonly used with Electron Microscopes because they have the highest magnification. Mrs. Degl 12 Staining Techniques are used to make it possible for an observer to see the structures of a cell easier under a microscope. 1. Iodine – used to stain the nucleus of a cell and preferably used to stain plant cells. Lugol’s (iodine) Solution is especially good for staining plant cells, like onion cells. Visible nuclei in onion cell 2. Methylene Blue- used to stain animal cells. This stain does not immediately kill the specimen, so it is ideal to observe animal cells. Cheek cell Mrs. Degl 13 Cell staining procedure (with methylene blue): 1. Place specimen on slide with forceps. 2. Lower the cover slip over the slide at a 45 degree angle to reduce the air bubbles. 3. Place a drop of water on the cover slip. 4. Place a drop of methylene blue beside and under one corner of the cover slip. 5. Place a small towel on the opposite side of the cover slip in the water beside the cover slip (This will draw the stain through the entire specimen within a few seconds and also remove any left over bubbles). 6. Observe. Mrs. Degl 14