Lab Microscope - Jocha
advertisement

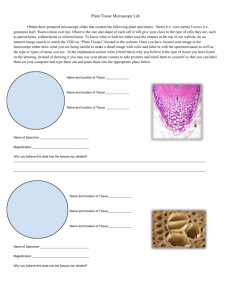
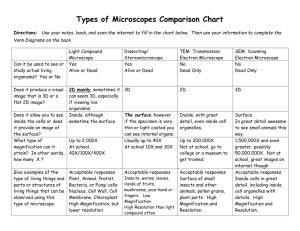
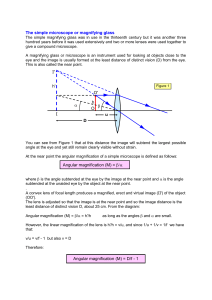
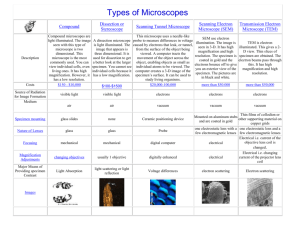
STUDY GUIDE FULLERTON COLLEGE – BIOLOGY 101 LAB: Microscope 1. Review the main distance units for the metric system and make sure you know how to make conversion between units. 2. Explain why the microscope used in the labs is called “light” or “compound” microscope. 3. Explain the difference between ocular and objective lenses. 4. What objective lens should be used first when observing a specimen? 5. Which one gives the best magnification? 6. How do you determine the total magnification power when using a light microscope? 7. Where is the light that illuminates the specimen coming from in a compound microscope? 8. What actually happens to the specimen when you move the mechanical stage to the right and left? 9. What happened to the orientation of the letter “e” when observed under the microscope? 10. Explain how you determined the size of the field of view (FOV) for 40X and 100X total magnification and the approximate size of the field of view with each lens 11. What happens to the size field of view (FOV) as you increase the magnification power from 40 (4X10), to 100 (10x10) to 400 (40x10)? 12. Make a list of all the different animal and plant cells observed with the microscope during the lab 13. What cell parts = cellular structures = organelles could you really observed in the animal cells? Explain the main function of each one of these organelles List all the examples of different ANIMAL cells observed during the lab 14. What cell parts = cellular structures = organelles could you really observe in the plant cells? Explain the main function of each one of these organelles List all the examples of different PLANT cells observed during the lab 15. Which cell parts allow differentiating an animal cell from a plant cell and which ones are common to all eukaryotic cells? Instructor: Jose Bava, Ph.D