201510_Enzyme Lab
advertisement

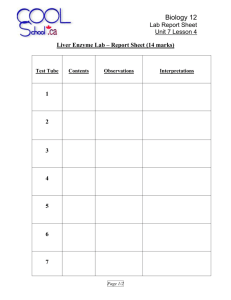
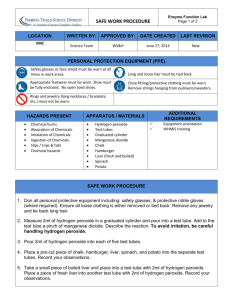
ENZYME LAB Name: _________________________ INTRODUCTION: Refer to textbook Page 51 to complete worksheet and prepare for upcoming lab Enzymes are proteins that ____________________ the chemical reactions of organisms. Without enzymes, most of the reactions in the cell would proceed too ______________ to maintain life. ACTIVATION ENERGY: All chemical reactions require energy for them to start. This energy is called _______________________________. Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy needed to start a reaction. The names of enzymes usually end in “-ase”. Thus ______________ catalyzes the breakdown of amylose into maltose subunits. An enzyme-catalyzed reaction is usually written with the names of the enzyme _________ the arrow. The enzyme amylase is found in your saliva and it’s job is to break down carbohydrates (at home, place a cracker in your mouth, don’t chew it and you will see that it will begin to dissolve) ENZYME ACTIVITY: In order to catalyze a reaction, an enzyme attaches to the reactants. We call the reactants _________________. The location where the substrate binds to the enzyme is called the ___________________________, and is usually a pocket or groove in the three-dimensional structure of the protein. Enzymes are very ______________ for the types of substrates they attach. This means that a different enzyme is needed for every reaction. As the substrate enters the active site, the protein changes shape to better fit the substrate. This is known as the ____________________________ of enzyme activity. ENZYME ACTIVITY and the ENVIRONMENT: _________________________________ and _____ have an effect on an enzyme’s activity. Look at figure 5 on page 53. A typical human enzyme works best at approximately ______. Enzymes have optimal pH levels. Enzyme A (pepsin) works best at pH = ___; but enzyme B (trypsin) works best at pH = _____. When temperatures are lower than the optimal temperature, the motion of the enzyme and the substrates is sluggish and reaction speed is reduced. Most human enzymes work best around _______, normal body temperature. INDUSTRIAL USES OF ENZYMES: In addition to the vital role they play in living cells, enzymes have many practical uses. In ______________, _______________, and ________________________ enzymes produced by yeast cells catalyze the conversion of glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide gas. RESEARCH QUESTION: Page 1 of 4 How do changes in temperature, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration , and pH affect the rate of catalase activity? REACTION: Without enzyme 2H2O2 [aq] 2H2O[l] + O2[g] [SLOW] 2H2O [l] + O2[g] [FAST] With Enzyme: catalase 2H2O2 [aq] MATERIALS: 3 test tubes and rack, test tube holder, 10-ml Graduated cylinder, 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, small pieces of liver PROCEDURES: Notes: Throughout this investigation you will estimate the rate of the reaction by measuring the height of oxygen bubbles produced Be sure to clean your stirring rod (and test tubes) between steps. You will need ruler to measure the height of oxygen bubbles Effect of the presence of Catalase Part A) Addition of Enzyme Place 5 ml of the 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into a clean test tube. 1. Using forceps place a small piece of liver into the test tube with the 5mL of hydrogen peroxide. Push the liver into the hydrogen peroxide solution with a stirring rod. 2. Observe and record results by measuring the height of oxygen bubbles 3. Discard the liquid into the waste beaker and put the liver into the garbage. Rinse out your test tube Part B: Effect of Temperature 1. Place 5 ml of 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into a test tube 2. Go to the teacher lab bench and get a piece of liver that has been heated (handle carefully) 3. Add the hot liver to the test tube with the peroxide 4. Observe and record your results 5. Discard the liquid and put the liver into the garbage 6. Pace 5 ml of 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into a test tube 7. Go to the teacher lab bench and get a piece of liver that has been cooled 8. Add the piece of cold liver to the test tube with the peroxide 9. Observe and record results 10. Discard the liquid and put the liver in the garbage 11. Rinse out your test tube Part C: Effect of Substrate Concentration 1. Place 5 ml of 1.5% hydrogen peroxide solution into a test tube – ensure that you are using the right concentration by reading the labels at the teacher lab bench 2. Push it into the hydrogen peroxide with a stirring rod 3. Observe and record results Discard the liquid and put the liver into the garbage 4. 5. 6. 7. Now obtain the 5 ml of 6 % hydrogen peroxide. (this is twice as strong as 3%) Place another piece of liver and place it in the test tube. Push it into the hydrogen peroxide with a stirring rod Observe and record results Discard the liquid and put the liver into the garbage Page 2 of 4 PART D: Effect of enzyme concentration 1. Place 5 ml of the 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into a clean test tube. 2. Using forceps place a 3 small pieces of liver into the test tube with the 5mL of hydrogen peroxide. Push the liver into the hydrogen peroxide solution with a stirring rod. 3. Observe and record results 4. Discard the liquid and put the liver into the garbage. Rinse out your test tube PART E: Effect of pH – Teacher demonstration OBSERVATION TABLE: Part Reaction Height of oxygen bubblesQualitative Observations (cm) A Liver plus 3% peroxide B (effect of changing temperature) Heated liver plus peroxide Cold liver plus peroxide C (effect of changing substrate concentration) Liver plus 1.5% peroxide Liver plus 6 % peroxide D (effect of changing enzyme concentration) 3 pieces of liver plus 3% peroxide E (effect of changing pH) Liver in acid Liver in base ANALYSIS: ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 3 of 4 ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ CONCLUSION: ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 4 of 4