Atomic+Bomb+Outline
advertisement

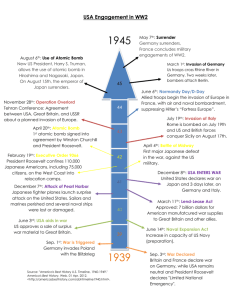
1 Ben, Alex, Luke, Brittany Period 3 The Atomic Bomb Outline KEY POINTS OF INFORMATION 1) The Manhattan Project General Information 1. A program created to develop atomic weapons, code-named: Manhattan Project 2. Began in December 1941 and ended in 1946 3. Extremely secret and few knew of its existence Origins 1. Albert Einstein wrote letter to FDR & helped him become aware of the potential uses of uranium 2. “Uranium Committee” created under National Research Defense Council 3. Committee eventually transformed into the Manhattan Project 4. Project was confirmed by FDR with out knowledge of congress & other officials 5. Funding paid from secret Presidential accounts Goals and Tasks 1. Research the nature and capabilities of atomic energy 2. Harness energy to create first atomic bomb People Involved 1. Army Corps of Engineers’ Manhattan District involved in bomb construction 2. Supervisor: General Leslie R. Roves 3. Head of Scientific Team: Physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer 4. Involved US and foreign scientists who worked at universities & industrial sites 5. Cost $2.2 Billion and employed over 600,000 workers Facilities and Development 1. Main Facility: Los Alamos, New Mexico 2. Other Sites: Oak Ridge, Tennessee and also Hanford, Washington 3. Research conducted in university laboratories (mainly Colombia and Berkley) 4. Constructed nuclear reactors to extract uranium from fossils and convert it into plutonium 2 5. Plutonium compressed in weapons so that chain reactions occur and create explosive power Results Produced From Project 1. Created first atomic bomb, tested on July 16, 1945 in New Mexico 2. Created the two operational bombs used against Japan a) Dropped “Little Boy” bomb on Hiroshima b) Dropped “Fatman” bomb on Nagasaki 2) Peace Negotiations Before Bombing 1. 3) Pros and Cons to Using the Atomic Bomb Pros 1. Mass killing had become almost acceptable 2. It would strike fear in the Nazis and Soviet Union 3. Assured complete surrender of the Japanese 4. The Japanese had refused to surrender and instead wanted to reach a peace agreement in which the Japanese would be able to rebuild their army and maybe attack again later 5. The U.S. thought that Japan deserved punishment for the acts that they committed toward China, for example the Rape of Nanking where hundreds of thousands of Chinese were killed Cons 1. Could be seen as immoral 2. It would kill thousands of innocent lives 3. Some thought that Japan’s defeat was inevitable and it could be found without the use of this weapon 4. Using this weapon would remove Americas “clear record” 5. Other alternatives were not tried before the use of the atom bomb 6. Although Japan would not accept defeat, they had started trying to talk to U.S. officials about peace 4) Aftermath of the Atomic Bomb / VJ Day VJ Day 3 1. The formal surrender took place on August 15, 1945 in Tokyo Bay 2. U.S. used island hopping in central and south west pacific in 1944 3. Subs were a big advantage to the US 4. Three battles final stages of liberation in the Philippines, invasions in Iwo Jima and Okinawa Philippines 1. First stage taking back of Leyte in December of 1944 2. Next liberation of Luzon Jan 2nd-8th 1945 US attacked 3. Suffered severe casualties due to kamikaze attacks 4. On the 9th US forces landed at Lingayen Gulf on the island west of Manila 5. Battle for Manila began in early February ended on March 4th 6. Casualties = 16,000 Japanese, 1,000 US, 100,000 Filipinos 7. US took manila Bay on April 17th 8. US took Yamashita August 15th 9. Total casualties US 33,000 Japan 190,000 10,000 captured Iwo Jima 1. February 18th land on shore to end of March 1945 2. Strategic land, for US bombers to resupply and to make emergency landings 3. 22,000 Japanese defended the island 4. December 8th 1944 bombers struck Iwo Jima for 72 days 5. 500 warships 75,000 Marines 6. Casualties 6,000 dead 17,000 wounded the Japanese all dead except for 216 prisoners Okinawa 1. Japan 77,000 people 2. US 1,200 warships 500,000 men 3. Attacked in April 4. Casualties 127,000 dead including civilians 400 warships sunk 5. 7,400 dead 32,000 wounded Atomic Bomb 4 1. First atomic bomb named little boy 4.5 miles destroyed gone, 66% of building in a 9.5 mile radius were destroyed 2. Dropped on august 6th 3. Target Hiroshima 4. 71,000 died and 68,000 injured 5. Second bomb Fat man Dropped on august 9th, target Nagasaki 6. Killed 40,000 and injured 25,000 5) North Korea and Weapons of Mass Destruction Background Information 1. In 2003 North Korea withdrew from the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty due to their intentions try and create nuclear weapons 2. This treaty was a pact among most countries that said that no making or research of nuclear weapons would be attempted North Korea’s Current Status 1. In April of 2009 North Korea was announced as a fully fledged nuclear power due their first successful test 2. Since April they have now made a total of six to eight nuclear weapons Possible Consequences 1. The US Government thinks that North Korea becoming a nuclear power threatens the peace of the world 2. They also think that if their leader Kim Jong-Il is not dealt with correctly then this “threat” could lead to nuclear war Conflict 1. The North Korean Government claims that they are just building up their own defense 2. Critics of the US government think that the US is being hypocritical due to the fact that the US has many more nuclear weapons than any other country in the world DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1) Do think that it was a good idea for the US to create the Manhattan Project to develop atomic weapons? 5 2) Should the US have continued peace negotiations or was it better to intervene and use deadly force? 3) After seeing the aftermaths of the bomb, do you think the US made the right decision? 4) Do you think that the US was right in setting off the two atomic bombs? 5) Do you think that the US has the right to intervene with North Korean projects to make nuclear weapons? PRESENTATION OUTLINE Topic Time Activities Presenter 1) The Manhattan Project 5 Minutes PowerPoint Ben 2) Peace Negotiations Before Bombing 5 Minutes PowerPoint Brittany 3) Consequences and Aftermath 5 Minutes PowerPoint Alex 4) Pros and Cons 2 Minutes PowerPoint Luke 5) Current Event 2 Minutes PowerPoint Luke 6) Movie and Questions 1 Minute Movie Group BREAKDOWN OF WORK BIBLIOGRAPHY 6 "The Atomic Bomb and the End of World War II: A Collection of Primary Sources." The George Washington University. Ed. William Burr. Web. 07 Jan. 2010. <http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB162/index.htm>. Dietrich, Bill. "Seattle Times Trinity Web: Dropping the Bomb." The Seattle Times | Seattle Times Newspaper. Web. 07 Jan. 2010. <http://seattletimes.nwsource.com/special/trinity/supplement/procon.html>. Sowell, Thomas. "The Morality of Dropping the Atomic Bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki by Thomas Sowell -- Capitalism Magazine." Capitalism Magazine Individual Rights are the Moral Basis of Society. Web. 07 Jan. 2010. <http://www.capmag.com/article.asp?ID=4362>.