Biology Pre-Reading Notes: Chapter 2
advertisement

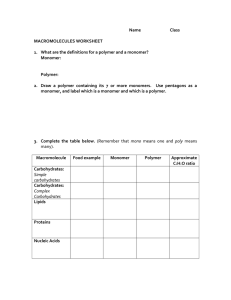
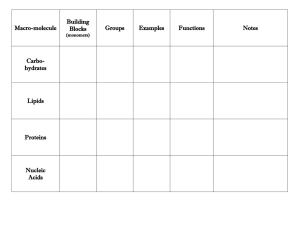
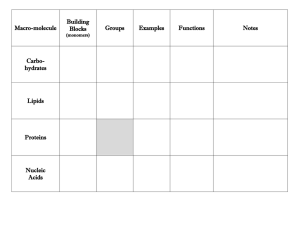
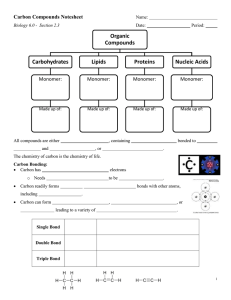
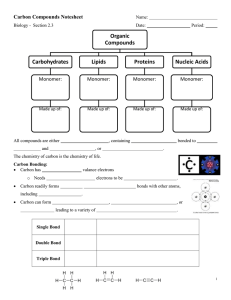
Chapter 2 Reading Guide Section 2-1 a. What are the subatomic particles of an atom? b. What are the characteristics of the subatomic particles? c. What is an element and give two examples of elements commonly found in the body. d. What information does the atomic number of an atom give? e. What subatomic particles compose an atom’s atomic mass? f. What does it mean to be a neutral element vs. an ion? g. Draw a picture of carbon showing it’s symbol, atomic number and atomic mass (weight). h. How are isotopes different? Give an example i. What is a covalent bond? Give an example j. What is an ionic bond? Give an example k. How are compounds related to molecules? l. What is the chemical formula for water? How many atoms of each element are there? m. What are Van der Waal’s forces and how do they hold molecules together? Section 2-2 a. Explain why water’s property to expand while freezing is essential to life on earth. b. What does mean for a molecule to be polar? c. Draw a picture of a water molecule and show its polar property. d. What are hydrogen bonds? e. What is the difference between cohesive and adhesive bonding? f. What are the components of a solution? g. How is a solution different from a suspension? h. What does pH measure? i. Explain what a pH of 7, below 7 and above 7 means. j. What are buffers and why are buffers important for the body’s homeostasis? Section 2-3 a. What does organic chemistry study? b. How many bonds can carbon form and what kind of bonding will it use? c. Draw a picture of a carbon molecule with single bond, double bond and triple bond. d. What is a monomer vs. a polymer? e. What is polymerization? f. Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things. g. List the elements found in carbohydrates. h. What is the main function of carbohydrates for living things? i. Name the 3 monosaccharides (monomers). j. Name the 3 important polysaccharides (polymers) made by living things. k. Draw a picture of a carbohydrate monomer and polymer. l. What elements are found in lipids? m. What types of lipids are there? n. List 3 functions of lipids by living things. o. What is the difference, structurally, between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? p. Draw and label the structure of a lipid. q. What are the elements found in nucleic acids? r. What are the monomers called? s. Name two polymer nucleic acids. t. List the function of nucleic acids. u. What are the elements found in proteins? v. What are the monomers? w. Describe the components of an amino acid. x. List the functions of proteins. y. Draw and label the structure of an amino acid. Section 2-4 a. What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? b. Describe the role of energy in chemical reactions. c. What is activation energy? d. What are enzymes, and how are they important to living things? e. What is a catalyst? f. What is an active site? g. What is a substrate? h. How does an enzyme catalyze a reaction? i. How can enzyme work be regulated? (i.e. turned on or off)