Name - Lyndhurst School District
advertisement

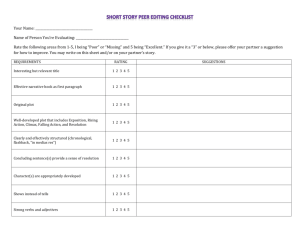
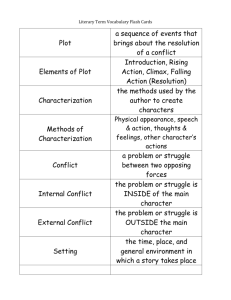
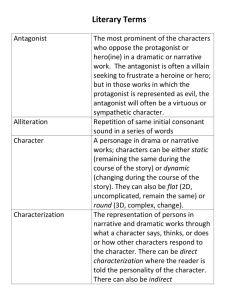
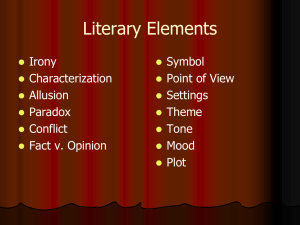
Literary Terms, Short Story: Part 1 1.) Speaker: the narrator/storyteller or “poetic voice” in a text 2.) Characterization: the representation of a character through description of his/her appearance, relationships, personality traits, actions, etc. 3.) Protagonist: the main character, usually “the good guy/girl” Example: Superman, Simba in The Lion King Example: 4.) Antagonist: the enemy to the main character; often known as “the bad guy/girl” Example: Gaston in Beauty and the Beast, Scar in The Lion King Example: 5.) Flat Character: minor character that lacks characterization; the audience knows little about this character 6.) Round Character: character whose personality is complex, like a real person’s, and the audience knows a lot about this character 7.) Static Character: character that does not undergo substantial change or growth 8.) Dynamic Character: a character who encounters conflict and is changed by it 9.) Foil: a character who differs in at least one way from another character Example: Bert is neat, but Ernie is messy. Example: 10.) Setting: the location, historical time, and social circumstances in which a story occurs Example: Beauty and the Beast is set in France. Les Miserables is set during the French Revolution. Example: 11.) Plot: the actions and events that take place in a work of fiction The plot is made up of the exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and denouement. 12.) Exposition: dialogue or description that provides background information about the characters and situation 13.) Rising Action: the part of a story where the plot or the conflict (problem) is further developed 14.) Climax: the most exciting point in the plot; the major turning point in a plot 15.) Falling Action: events that take place after, and as a result of, the climax 16.) Denouement: the outcome or ending 17.) Freytag’s Pyramid: the storytelling structure that includes an exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and denouement 18.) Conflict: the problem in the plot 19.) Vignette: a very short piece of narrative writing that expresses a complete thought 20.) Symbol: something concrete that represents something abstract Example: A baby bottle can represent youth. Example: A wreath can represent peace or the holiday season. 21.) Theme: a universal message or lesson about life or society Example: Siblings are a great source of support in times of difficulty. 22.) Flâneur: people-watcher 23.) Point of View: the perspective from which a story gets told (who is telling the story) 3 Points of View 24.) First Person Point of View: the story is told from the “I” perspective Benefits? Drawbacks? 25.) Second Person Point of View: the narrator addresses the audience as “you” Benefits? Drawbacks? 26.) Third Person Point of View: the narrator is not a character in the story, but tells an account of what is going on Benefits? Drawbacks? 27.) 6 Types of Conflict (problems) Person versus Person Person versus Nature Person versus Society (a group, world, or circumstance) Person versus Self Person versus Supernatural Person versus Machine/Technology 28.) Dialogue: conversation between two or more characters helps to explain relationships between characters may illustrate a character’s mood, temper, or personality may be humorous or set a specific tone for the writing breaks up paragraphs of description 29.) Pathetic Fallacy: when the weather mirrors a character’s emotions Example: When the character is scared, it happens to be a stormy night. Example: When the character is happy, it happens to be a sunny day. 3 Types of Irony 30.) Situational Irony: when the opposite of what is expected occurs Example: The boy thought he aced an exam, but he actually failed. Example: Lily’s brand new cell phone is not turning on. 31.) Dramatic Irony: when the audience knows something that a character or characters do not know Example: The audience knows the family won the lottery, but the family has not found out yet. 32.) Verbal Irony: when the speaker says one thing, but means another; sarcasm Example: Saying “Boy, it’s hot,” when it is snowing out. Types of Characterization 33.) Direct Characterization: the writer tells the reader exactly what the character is like or what a person’s motives are * My friend is hard-working. 34.) Indirect Characterization: the writer offers an example or story that allows the reader to interpret for him/herself who the character is * My friend worked for hours on the project. 35.) Deus ex Machina: a person or feature that suddenly appears in a work of fiction and provides a contrived or unbelievable solution to a problem. 36.) Extrovert: an outgoing, expressive person who prefers to be around people 37.) Introvert: a person who prefers to be by him/herself; someone quiet and reserved 38.) Optimist: a person who has a positive viewpoint; “sees the glass as half full” 39.) Pessimist: a person who has a negative viewpoint; “sees the glass as half empty” 40.) Transitional Words: words that help a writer move between topics. Examples: