WELCOME TO … ELEMENTS OF A SHORT STORY GET READY TO WRITE!!!
advertisement

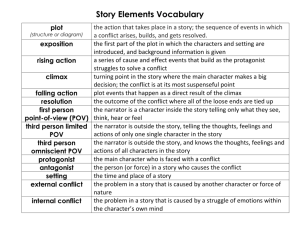
WELCOME TO … ELEMENTS OF A SHORT STORY GET READY TO WRITE!!! THEME THEME: the central thought or idea upon which a story is based; usually a comment about life or human nature. CHARACTERIZATION a portrayal of character through what they say and do and through what other characters say about them in a story. CHARACTERIZATION: CHARACTERIZATION • DIRECT CHARACTERIZATION: when the author tells you what characters are like through description. • INDIRECT CHARACTERIZATION: when the author shows you what characters are like through their thoughts, their speech, their actions, and the reactions of other characters around them. CHARACTER CHARACTER: a fictional person in the story. • PROTAGONIST: the character with a problem in the story. The main character or force in a story or play. • ANTAGONIST: the person or thing fighting against the protagonist of a story or play. PLOT PLOT: THE SEQUENCE OF EVENTS OR ACTIONS IN A STORY, NOVEL, OR NARRATIVE POEM. PLOT LINE PLOT LINE - shows the actions or events in a story. THE Plot Line EXPOSITION EXPOSITION In fiction, a part of a story (usually the beginning) where the author tells the background material which the reader must know about the characters and events in order to understand the problem to be solved. EXPOSITION SETTING SETTING: the time and place in which the action of a short story, novel, play or narrative poem is presented. COMPLICATIONS COMPLICATIONS (also called Rising Action): point of the story when various problems happen. Complications CLIMAX CLIMAX: sometimes the highest point of excitement/interest, or the turning point of the story. Climax DENOUEMENT FALLING ACTION: the part of the story which follows the climax or turning point: it contains the action or dialogue necessary to lead the story to a resolution or ending. Falling action DENOUEMENT RESOLUTION: THE FINAL OUTCOME OF THE CONFLICT. Resolution CONFLICT CONFLICT: a problem or struggle between opposing forces, ideas, or significant characters that forms the basis of the plot of a story or play. There are two (2) types of conflict TYPES OF CONFLICT EXTERNAL CONFLICT: A struggle with a force OUTSIDE of oneself. Kinds: man vs. man, man vs. nature & man vs. society INTERNAL CONFLICT: A struggle WITHIN a character. Kind: Man vs. himself/herself KINDS OF CONFLICT External Conflict External Conflict: •Man vs. Man: the leading character struggles with his/her physical strength against other men/women. KINDS OF CONFLICT External Conflict •Man vs. Society: The leading character struggles against ideas, practices, or customs of other people. KINDS OF CONFLICT External Conflict •Man vs. Nature: the leading character struggles against fate, or the circumstances of life facing him/her. (ex. floods, hurricanes, etc.) KINDS OF CONFLICT Internal Conflict •Man vs. Himself/Herself: the leading character struggles with his/her own soul, ideas of right or wrong, physical limitations, choices, etc. POINT OF VIEW POINT OF VIEW: the outlook or position from which a story is told. KINDS OF P.O.V. First Person POV: the narrator is a character in the story and uses first person pronouns such as I, me, we, us. KINDS OF P.O.V. Third Person POV: the narrator is not a character; he or she uses third-person pronouns such as he, she, it , they, and them. KINDS OF P.O.V. Third Person Omniscient (allknowing) POV: allows the narrator to relate the thoughts and feelings of several, if not all, the story’s characters. KINDS OF P.O.V. Third Person Limited POV: narrator tells the reader the thoughts, observations, and feelings of ONE of the story’s characters. The End!! HELPFUL HINT: STUDY THIS INFORMATION! YOU WILL NEED IT TO SURVIVE THE LITERATURE SECTIONS IN 7TH GRADE ENGLISH!!