HealthPath Math - Degrees-bed positioning
advertisement

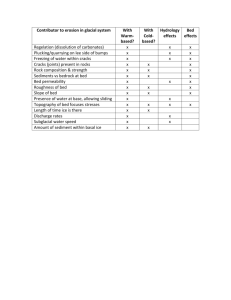
Understanding and Applying Degrees (spatial) and Angles in Health Care Settings When most of us think of degrees, we think of it in terms of temperature, body temperature and environmental temperature. For example, 98.6 degrees is normal adult body temperature. 32 degrees is freezing temperature. In this lesson we will be looking at degrees in another way. Degrees are also used in Geometry to describe space. Circles are made up of 360 degrees and a half circle is made up of 180 degrees. If you have 2 points on a circle and draw lines from each point to the center of the circle, an angle is formed. 90 degrees 0 degrees 360 degrees 180 degrees 270 degrees How many degrees does ¼ circle have? How about ¾ circle? Where is 30 degrees on a circle? Where is 120 degrees on a circle? Pilots, athletes and coaches, dancers, engineers all refer to space in degrees and/or angles. For example, a pilot might announce to a plane full of passengers, “Ladies and Gentlemen, we will be turning 90 degrees to our right as we head east to Boise.” Looking at the airplane, show where it will turn if it is turning 90 degrees to the right. Nurses, Nursing Assistants, Physical Therapists and Physical Therapy Assistants, and Occupational Therapists all use spatial degrees at times to describe and implement patient care plan needs. You will have some opportunities to apply spatial degrees and angles to specific health care situations. Health Care Application: Bed Positions There are many bed positions, but very often patients who have breathing and swallowing problems, recovering from different surgeries, will need to be in specific positions. Here are the various bed positions: Flat – Is as described, flat on the back, stomach, side – 180 degrees. Fowler’s position - Is a semi-sitting position with the head of the bed raised between 45 and 60 degrees. High Fowler’s position – Is a semi-sitting position with the head of the bed raised 60 to 90 degrees. Semi-Fowler’s position – Is the head of the bed raised 30 degrees. Orthopneic position – Is with the patient in High Fowlers position and leaning slightly forward. 1. Looking at the 5 bed placement terms, please draw/illustrate each one with a simple line drawing, as shown for Flat Fowler’s High Fowler’s Semi-Fowler’s ___________ Orthopneic 2. You are carrying through the following care plans for bed positions for various patients. Please illustrate/line draw the bed positions in each of the following examples. a. Mrs. Smith is a stroke at risk of choking and needs help being fed her meals. The care plan specifies bed position at 90 degrees for feeding. Please illustrate Mrs. Smith’s bed position. b. Mr. Martinez was just admitted with a spinal cord injury. The care plan specifies bed position at 180 degrees. Please illustrate Mr. Martinez’s bed position. c. Mr. Chen has emphysema. The care plan specifies orthopneic position as much as possible during waking hours. Please illustrate Mr. Chen’s bed position. d. Miss Peterson had her thyroid removed. The care plan specifies bed position at 70 degrees. Please illustrate Miss Peterson’s bed position. e. Mrs. Kaur is recovering from open heart surgery. The care plan specifies bed position at 20 degrees. Please illustrate Mrs. Kaur’s bed position.