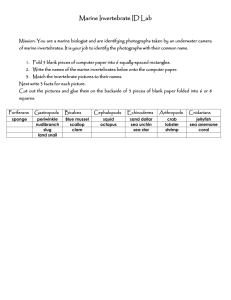
Invertebrate Project
advertisement

Animal Unit Chapters 32-34. Chapter 32: Key features of animals Development of animals from fertilized egg to adult Germ layers: 3 types and what tissues they will become Parazoa vs. Eumetazoa, Protostome vs. Deuterostome, diploblastic vs. triploblastic Acoelomate vs. Pseudocoelomate vs. Eucoeomate Germ layers relate How the body is divided up for study Ventral/ Dorsal Posterior/ Anterior Inferior/ Superior Medial/ Distal Midsaggital plane Types of symmetry Chatper 33: See Invertebrate project Chapter 34: Vertebrates (notes will be provided) Human evolution Invertebrate Project You and a partner (or 2) are assigned a group of invertebrates to research and present to the class. You may choose how you would like to present the information – PowerPoint, video, booklet, brochure, poster. Remember that the entire class will be responsible for what you present to them. Handouts are required. All handouts should be typed and one page. Pictures are encouraged. You will have 15 minutes to present. Each presentation must include information on the following for the assigned group of invertebrates: type of symmetry reproduction/ life cycle number of germ layers and coelom specialized tissues type of body development 5 examples of organisms movement *****interesting stories ***** In addition, there are required terms to be covered for each group of invertebrates. After the presentation, you should be prepared to quiz the group through questions or some kind of game for five minutes. At the 20 minute mark, the lesson must be completed. Here are the group assignments and the required terms: First presentations: Team 1 and Team 2 on Thursday Feb 14 Team 3 and Team 4 on Friday Feb 15 Team 5 and Team 6 on Wednesday Feb 20 GRADE: 40 points on your animals test. : Accuracy, usability to the rest of the class, organization of handout will be the three major components considered. Team 1: Porifera: - spongocoel - osculum - choanocyte - ostia - amoebocyte - spongin - spicules - porocytes Cnideria and Ctenophora: - gastrovascular cavity - comb - life cycle of jellyfish - polyp - colloblasts - portuguese man-o-war colony - medusa - cnidocytes - coral reef types/ formation - nematocysts - mesoglea Team 2 Platyhelminthes: - pharynx - gastrovascular cavity (highly branched) - Schistosoma life cycle - eye spots - ventral nerve chord - Trichinella life cycle - parasite - ganglia - scolex Rotifera and Nematoda: - parthenogenesis - complete digestive tract - cuticle - hydrostatic skeleton - longitudinal muscles Nemertea and Lophophorate: - proboscis apparatus - complete digestive tract - lophophore - closed circulatory system Team 3 Mollusca and Annelida – - foot - trochophore - setae - differences in lifestyle between squid/octopus - mantle - visceral mass - clitellum - classes of mollusks - radula - torsion - crop - classes of annelids - septa - metanephridia Team 4 Arthropoda: - cuticle - exoskeleton - book lungs - molting - open circulatory system - different classes - chelicerae - mandibles - choose 5 important orders of insects - antennae - compound eyes - malpighian tubules - metamorphosis (complete and incomplete) - tracheal system - spiracles Team 5 Echinodermata - tube feet - water vascular system - how tube feet are extended and used - spines - 2 stomachs of starfish - 5 classes of echinoderms - pentaradial symmetry Team 6 Chordata - notochord dorsal hollow nerve cord pharyngeal gill slits post anal tail - 3 subphyla - 7 classes of vertebrata - phylogenic tree of chordate - Archaeopteryx and Protavis