notes
advertisement

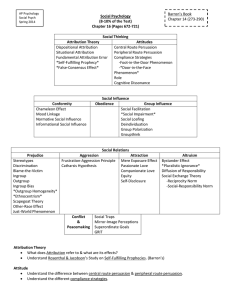
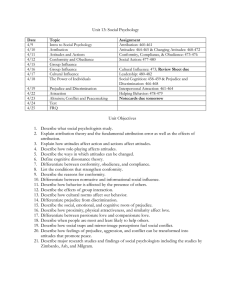
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIT MONDAY January 6 7 8 9 10 Social – Attitudes & Attributions Social – Conformity & Obedience Social – Group Behavior Social – Aggression Social –Prejudice HW: Read & notes p.650-657 (Conformity & Obedience) HW: Read & notes p.685-687 (Altruism) HW: Read & notes p.678-685 (Attraction) HW: Read & notes p.655-692 (Conflict & Peacemaking) HW: UNIT 9 ONLINE ASSESSMENT 13 Last Day of 2nd Semester 14 15 16 17 AP Exam Discussion & Review TUESDAY FINALS – Periods 1, 2, 4 WEDNESDAY FINALS – Periods 3, 5, 6 THURSDAY FINALS – Periods 7, 8 FRIDAY RELAX!!!!!!!!!! HW: Study for Finals! Attitudes & Actions (p.646-650): Explain the relationship between attitudes and behaviors. *Three Components of Attitudes: Elaboration likelihood model Central route to persuasion: Peripheral route to persuasion: Many streams of evidence confirm that attitudes follow behavior! Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon: Door-in-the-Face: How did Zimbardo’s prison study demonstrate that role-playing affects attitudes? Cognitive Dissonance Theory: Attributing Behavior (p.644-645): List and describe attribution judgments and biases. *Social Schemas: Dispositional (Internal) Attribution: Situational (External) Attribution: Fundamental Attribution Error: Self-serving bias: HW: Social Influence: Conformity & Obedience (p.650-657): Explain the concepts of obedience & conformity through the research of Asch & Milgram. Chameleon effect: Solomon Asch’s Line Study (design, results): Conditions that Strengthen Conformity 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Reasons for Conforming Normative Social Influence: Information Social Influence: Obedience Stanley Milgram’s experiment (design, results): Obedience was highest when….1) 2) 3) 4) HW: Altruism (p.685-687): Trace the development of pro-social behaviors. Altruism: Bystander effect (diffusion of responsibility): Best odds of helping someone occur when…. Norms for helping Social exchange theory: Reciprocity norm: Social-responsibility norm: Social Influence: Group Behavior (p.657-664): Discuss how group interaction can facilitate group polarization and groupthink. Social facilitation: Social loafing: Deindividuation: Group polarization: Groupthink: *Factors the increase likelihood of groupthink Interaction between social control & personal control Minority influence: HW: Attraction (p.678-685): Assess the different theories of attraction and love. Proximity Mere exposure effect: Physical Attractiveness Similarity Reward theory of attraction: Hatfield’s “passionate love” v. “companionate love” Equity Self-disclosure Social Relations: Aggression (p.670-677): Discuss the issues and factors related to aggression. Biology of Aggression Genetic Influences Neural Influences Biochemical Influences Psychological & Social-Cultural Factors in Aggression Aversive Events Frustration-aggression principle: Social & cultural influences Observing models of aggression Acquiring social scripts Do video games teach, or release, violence? HW: Conflict & Peacemaking (p.688-692): Trace the development & resolution of group conflict. Social traps: Enemy perceptions Mirror-image perceptions: Self-fulfilling prophecies: Reducing Conflict: Contact Cooperation Superordinate goals: Communication Conciliation GRIT: Social Relations: Prejudice (p.664-670): Describe the factors that contribute to cultural, ethnic, and gender prejudice & discrimination. Prejudice v. stereotypes v. discrimination Social Roots of Prejudice Social inequities Ingroup bias: Emotional Roots of Prejudice Scapegoat theory: Cognitive Roots of Prejudice Outgroup homogeneity: Other-race effect (own-race bias): Just World Phenomenon: