AP Psychology Outline Chapter 18: Social Psychology OVER→
advertisement

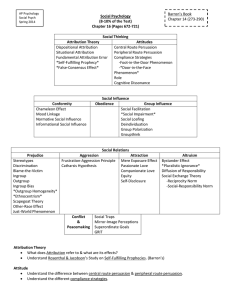
AP Psychology Outline Chapter 18: Social Psychology I. Social Psychology a. What do Social Psychologists study? An example? b. Attributing Behaviors to Persons or Situations i. What was the theory proposed by Fritz Heider? Define this theory. ii. What is the fundamental attribution error? Example of how it works? iii. What are some political effects of attribution? c. Attitudes and Actions i. What is an example of how attitude affected action? ii. What is the foot-in-door-phenomenon? How does this demonstrate an action affecting attitude? iii. How does role-playing affect attitude? Give an example? iv. What is cognitive dissonance? How is modern war an example? II. Social Influence a. Conformity and Obedience i. How are the chameleon effect and mood linkage examples of conformity? (Define and answer) ii. How did Solomon Asch's experiment demonstrate conformity? iii. How do normative social influence and informational social influence demonstrate reasons for conforming? (Define and answer) iv. What happened in Stanley Milgram's experiment? How does this demonstrate obedience? How has the outcome been attributed to real life events? b. Group Influence i. What is social facilitation? How is the comedy room an example of this? ii. What is social loafing? Why does this happen so easily? iii. What is deindividuation? iv. How is group polarization an effect of group interaction? v. What is the danger in groupthink? How has it been seen in American history? vi. Where have we seen minority influence? (Define and example) III. Social Relations a. What are prejudice, stereotypes and discrimination? How do they differ from one another? b. What are some examples of 'automatic prejudice?' c. Social Roots of Prejudice i. How are social inequities a cause of prejudice? ii. What is ingroup bias? How does it contribute to prejudice? iii. What is the scapegoat theory? How is it an emotional root of prejudice? iv. What are some cognitive roots of prejudice? v. How does one use the just-world phenomenon to rationalize prejudice? IV. Aggression a. Biology of aggression i. What are some genetic and neural influences on aggression? ii. How are biochemical influences related to the biology of aggression? b. Psychology of aggression i. What is the frustration-aggression principle? ii. What are some ways in which people learn aggression is rewarding? iii. How do models of aggression influence the way we respond? c. What evidence is there regarding video games and violence? OVER V. Conflict a. What is conflict? Do the elements change from one situation to the next? b. What are social traps? How does the game matrix demonstrate this concept? VI. Attraction a. What does proximity have to do with our attraction to others? i. What is the mere exposure effect? ii. Are we more favorable towards good looking people? Why/how so? iii. How does similarity factor in to who we are attracted to? b. Love i. What is the difference between romantic love, passionate love and companionate love? How does each factor in our relationships? ii. What are equity and self-disclosure in regards to companionate love? VII. Altruism a. What is altruism? b. What is the bystander effect? How has this been demonstrated? c. Helping others i. What is the social-exchange theory? The reciprocity norm? The social-responsibility norm? How do these demonstrate reasons for helping others? VIII. Peacemaking a. What are superordinate goals? b. How does GRIT help to reduce tensions?