Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept

Answers to Review Questions - Chapter 39
1.
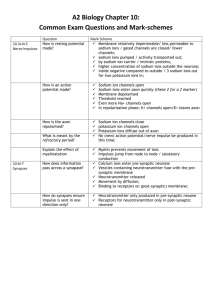
What are the functions of a) astrocytes and b) microglia?
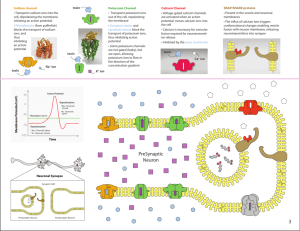
(a) Astrocytes provide neurons with glucose (i.e. give nourishment) and give structural support.
(b) Microglia remove cell debris by phagocytosis.
2.
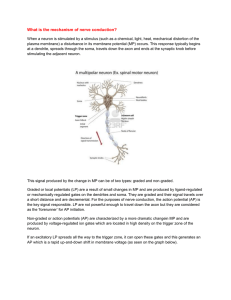
What are the functions of a) dendrites, b) synaptic terminals, and c) axons?
(a) Dendrites receive stimuli and send signals to the cell body.
(b) Synaptic terminals release neurotransmitters.
(c) The myelin sheath insulates an axon (speeds transmission of signals).
3.
How is a neuron different from a nerve?
A nerve consists of many neurons wrapped together.
4.
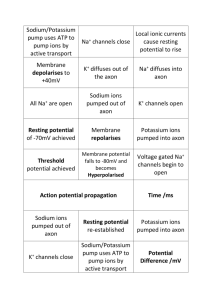
How do ion channels and sodium-potassium pumps contribute to the resting membrane potential?
The leaking of potassium ions through passive ion channels is the primary factor involved in establishing the resting potential, although the leaking of sodium ions is involved to a lesser extent. To counteract this leaking, the operation of the sodium-potassium pump maintains the gradients of sodium and potassium and thus the resting potential of the neuron.
5.
What sequence of events occurs when threshold level is exceeded in a neuron?
Once the threshold level is exceeded, the sodium gates open and sodium ions enter the cell. Then the sodium gates close, the potassium gates open, potassium ions flow out of the cell, and the potassium gates close.
6.
How do voltage-activated ion channels work?
Voltage-activated ion channels have charged regions that are sensitive to voltage.
When the voltage across the membrane changes, these channels open and close.
7.
What are the benefits of saltatory conduction compared with continuous conduction?
Saltatory conduction is much faster than continuous conduction and requires less energy.